Nerve06/central nervous system/basics of the motor pathway
| The motor (efferent) action potentials descend from the cerebral cortex to the skeletal muscles via two (upper and lower) (primary and secondary) motor neurons. |
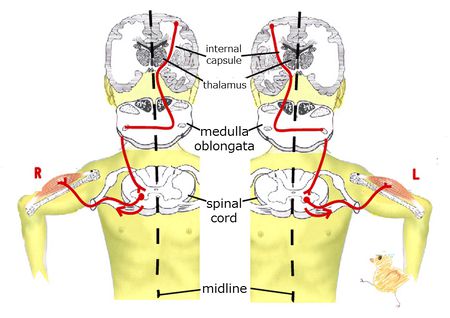
The cell body for the primary (upper) motor neuron is in the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex.
The descending fibers of the primary motor neurons pass through the internal capsule, but not the thalamus.
The primary motor neuron fibers cross the right-left midline.
The primary motor neuron forms a synapse with the secondary motor neuron in the anterior horn of the spinal cord.
The secondary motor neuron fibers leave the spinal cord from the anterior root and innervate the skeletal muscle.
Challenge Quiz
The cell body of the primary (upper) motor neuron is located in the anterior horn posterior horn posterior root ganglion thalamus precentral gyrus postcentral gyrus internal capsule .
The cell body of the secondary (lower) motor neuron is located in the anterior horn posterior horn posterior root ganglion thalamus precentral gyrus postcentral gyrus internal capsule .
The primary (upper) secondary (lower) cross the right-left midline.
The fiber of the secondary (lower) motor neuron, after leaving the spinal cord, directly reaches change neurons and then reach the skeletal muscles.
The motor descending pathway does does not pass through the internal capsule.
The motor descending pathway does does not pass through the thalamus.
The afferent efferent action potential for moving the RIGHT foot is generated in the right left postcentral gyrus precentral gyrus , and then passes through the right left internal capsule, right left side anterior posterior horn, right left side anterior posterior root, and reaches the skeletal muscle.
The afferent efferent action potential for moving the LEFT foot is generated in the right left postcentral gyrus precentral gyrus , and then passes through the right left internal capsule, right left side anterior posterior horn, right left side anterior posterior root, and reaches the skeletal muscle.