呼吸/respiratory cycle in English/Pleural pressure
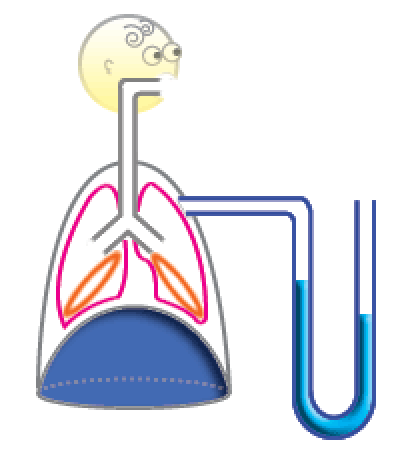
The thin liquid film between the chest wall and lungs, keeps the lungs from being pulled away from the chest wall. Because of inward elastic force of the lungs and the outward elastic forces of the chest wall, the pressure between the lungs and the chest wall is negative.
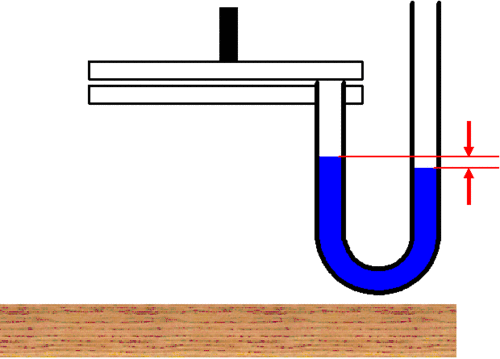
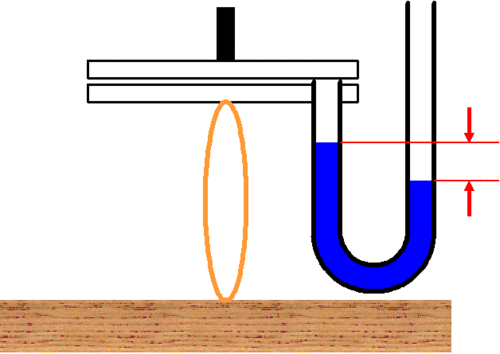
The chest wall has outward elasticity, which (when the respiratory muscles are relaxed and there is no respiratory movement) balances with the inward elasticity of the lungs. The pleural pressure, which is the pressure between the lungs and the chest wall, is negative (note that the blue pressure gauge on the lung side is elevated).
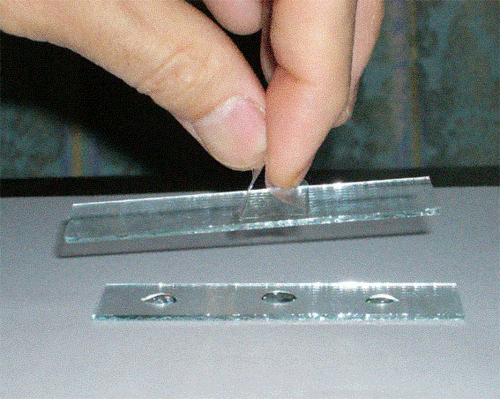
For example: One glass slide, with a handle, is placed on top of another glass slide, and there is water inbetween the two.
After placing the upper one on top of the lower one, lifting the upper one will lift the lower one as well.
Without water, the lower slide will not be lifted.
Naturally, the pressure between the two glass slides is negative, the strength being equivalent to the weight of the glass.
Let's assume that the lower slide is attached to a rubber band, which is also attached to the desk. If the rubber band is stretched, the negative pressure between the two slides would be equivalent to the weight of the glass and the elasticity of the rubber band.
The relation between the chest wall and the lungs is similar to this example. The lungs are like the lower slide being pulled with a fixed rubber band. The chest wall is like the upper slide with a handle. There is liquid between the chest wall and lungs. This liquid, which is in a thin film-like form, keeps the two together. The inward elastic force in the lungs works towards decreasing the lung volume (Note that the rubber bands in the lungs are lightly stretched). The outward elastic force of the chest wall increases the volumes of the thoracic cavity and of the lungs. The pressure betweeen the lungs and chest wall (pleural pressure) is negative (note that the blue pressure gauge, with its tip between the lung and chest wall, is elevated on the lung side, compared to the outer-side, which is opened and thus indicates the atmospheric pressure).
| lung volume | min |
| inward elastic force of the lungs | min |
| negative pleural pressure | min |
(within one quiet respiratory cycle)
Challenge Quiz
There is liquid air between the lungs and the chest wall.
The chest wall has inward outward elastic force (when the respiratory muscles are relaxed and there is no respiratory movement).
The pressure between the lungs and the chest wall is the pleural pressure alveolar pressure .
The pleural pressure is negative compared equal positive compared to the atmospheric pressure (when the respiratory muscles are relaxed and there is no respiratory movement).