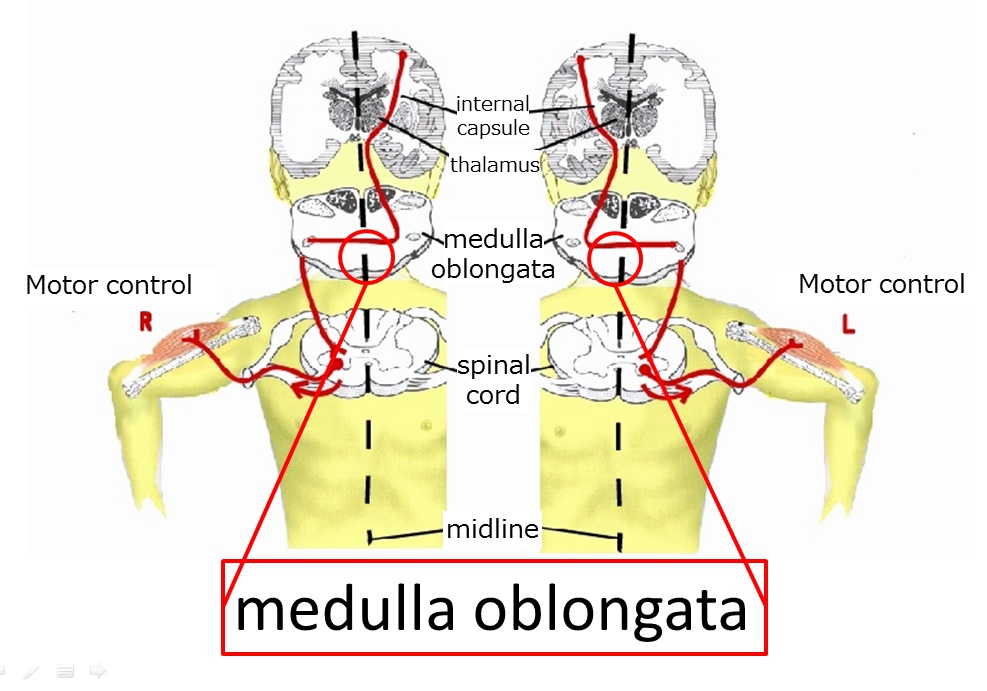
Nerve05/disorders of the spinal cord and optic pathway/descending pathway of motor innervation
The descending pathway for voluntary movement starts in the primary motor cortex, in the precentral gyrus in the frontal lobe, travels through the internal capsule, does not synapse, but rather crosses the right-left midline to the other side in the medulla oblongata. Then the pathway descends through the lateral funiculus (column), synapses with the 2nd motor neuron in the anterior horn. This pathway is called the corticospinal tract (pyramidal tract). The fiber of that neuron leaves the spinal cord through the anterior root, becomes a peripheral nerve fiber, and innervates the skeletal muscle.
Challenge Quiz
The corticospinal tract (pyramidal tract) travels through the anterior lateral posterior funiculus (column) of the spinal cord.
The voluntary movement pathway travels through the spinothalamic tract posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway corticospinal tract (pyramidal tract) .
The descending pathway for the voluntary movement starts in the primary somatosensory cortex primary motor cortex in the precentral gyrus postcentral gyrus in the frontal temporal parietal occipital lobe, travels through the basal ganglia internal capsule limbic system , synapses and then crosses the right-left midline to the other side does not synapse, but rather crosses the right-left midline to the other side in the cerebral cortex basal ganglia hypothalamus medulla oblongata spinal cord . Then the pathway descends through the anterior lateral posterior funiculus (column), synapses with the 1st 2nd 3rd motor neuron in the anterior posterior horn. The fiber of that neuron leaves the spinal cord through the anterior posterior root, becomes a central peripheral nerve fiber, and innervates the skeletal muscle.