Endocrinology/CaHomeostasis/BloodCaandPTH
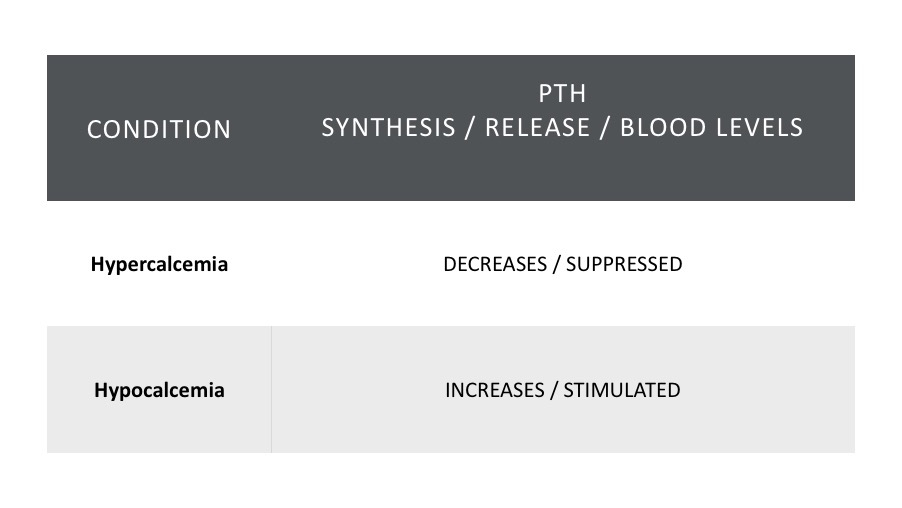
| When blood calcium levels rise, PTH levels decrease, this returns calcium levels back to normal. When blood calcium levels drop, PTH levels increase, this returns calcium levels to normal. PTH controls blood calcium levels. |
The effect of blood calcium levels on parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion
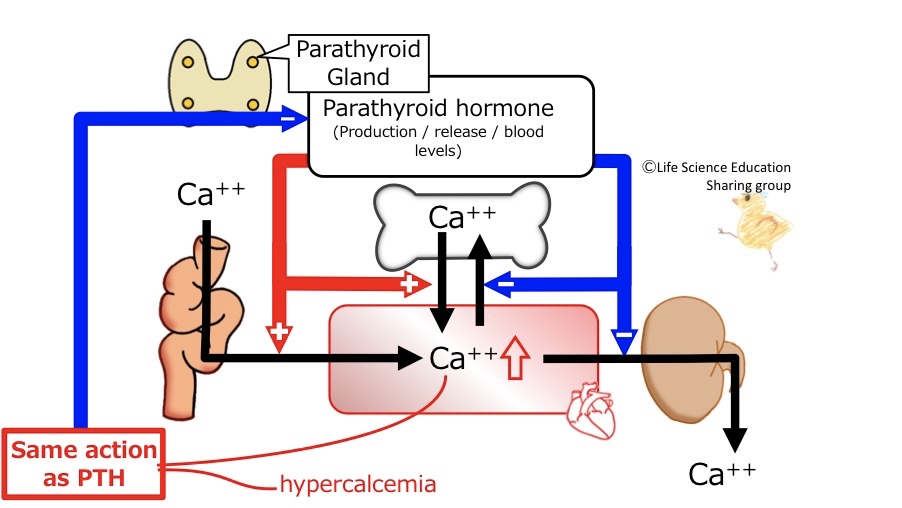
During hypercalcemia you are observing the same response as what you would see with excessive PTH release. The rules of negative feedback tell us therefore that hypercalcemia will lead to an inhibition of PTH formation and secretion, decreasing PTH blood levels which in turn will bring Ca2+ levels back to normal.
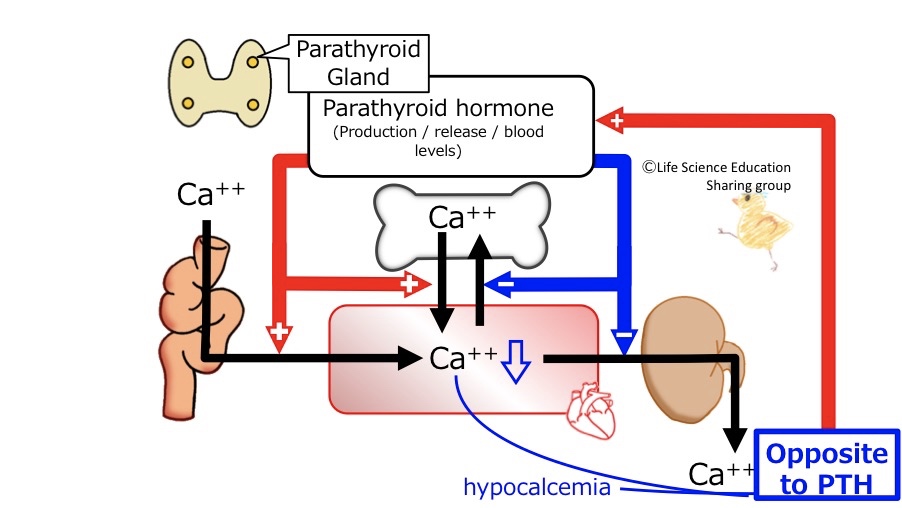
During hypocalcemia you are observing the opposite response to what you would see with excessive release of PTH. The rules of negative feedback tell us therefore that hypocalcemia will lead to a stimulation of PTH formation and secretion, increasing PTH blood levels which in turn will bring Ca2+ levels back to normal.
PTH levels in the blood are controlled by blood Ca2+ levels in the following manner.
Challenge Quiz
You must wait for the CORRECT! 正確!
<GIFT> //LEVEL:2 //RAND With respect to the negative feedback control, the secretion of parathyroid hormone is adjusted by: {=It’s physiological effect ~It’s blood concentration}
//LEVEL:2 //RAND Hypercalcemia indicates a(n) {=Elevated~Depressed} blood calcium concentration. This is the {=Same~Opposite} as/of the response to parathyroid hormone. The response of the parathyroid gland to hypercalcemia is to {Increase~=Decrease} PTH synthesis and release.
//LEVEL:2
//RAND
Hypocalcemia indicates a(n) {Elevated~=Depressed} blood calcium concentration. This is the {Same~=Opposite} as/of the response to parathyroid hormone. The response of the parathyroid gland to hypercalcemia is to {=Increase~Decrease} PTH synthesis and release.
//LEVEL:2 //RAND A decrease in blood levels of parathyroid hormone will cause blood calcium levels to {Increase~=Decrease}
//LEVEL:2 //RAND An increase in blood levels of parathyroid hormone will cause blood calcium levels to {=Increase~Decrease}