呼吸/respiratory cycle in English/Lung volume, pressure inside the lungs and air flow-2
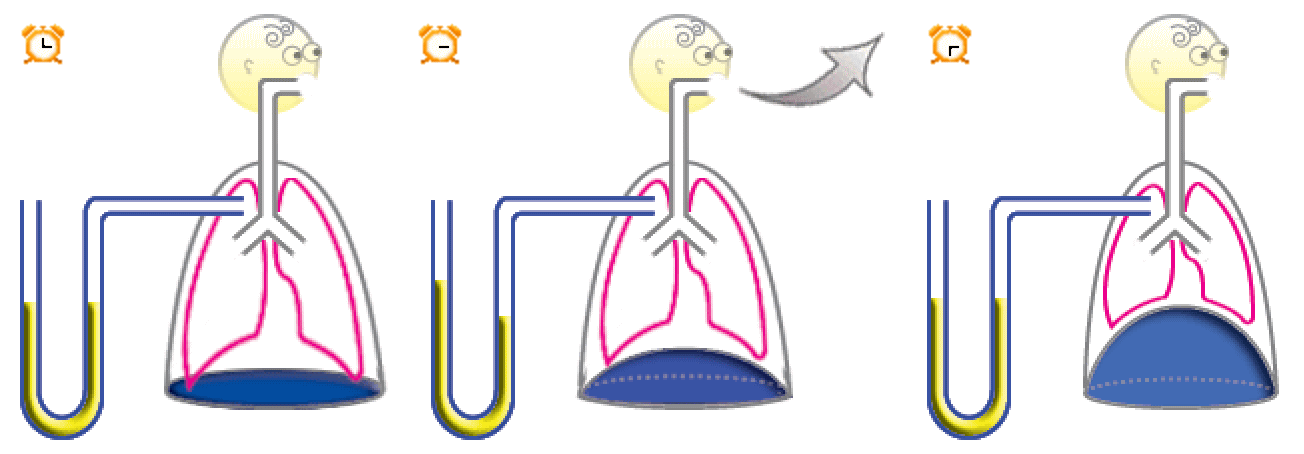
When the lungs decrease in volume, the pressure inside the lungs (alveolar pressure) becomes positive compared to the atmospheric pressure. Due to the positive pressure, the gas inside the lungs flows out. When the lungs remain decreased at a constant volume, the positive pressure disappears and the flow ceases.
When the lungs decrease in volume, due to decrease in the thoracic cavity volume from inspiratory muscle relaxation, the pressure inside the lungs (alveolar pressure) is positive compared to the atmospheric pressure. Note that the yellow pressure gauge is lower on the lung side, compared to the outer-side, which is open and thus indicates the atmospheric pressure. When the lungs remain decreased at a constant volume, the positive pressure disappears and the flow ceases.
As mentioned in a former step, the decrease in lung volume is due to the elasticity of the lungs.
| lung volume (within one quiet respiratory cycle) | max | max→min | min |
| pressure inside the lungs (alveolar pressure) | atmospheric pressure | positive pressure | atmospheric pressure |
| flow | none | out | none |
Challenge Quiz
When the lungs decrease in volume.the pressure inside the lungs (alveolar pressure) is negative compared equal positive compared to the atmospheric pressure.
When the lungs are kept at a decreased volume.the pressure inside the lungs (alveolar pressure) is negative compared equal positive compared to the atmospheric pressure.
When the lungs decrease in volume. gas (air) flows in there is no gas flow gas flows out .
When the lungs are kept at a decreased volume. gas (air) flows in there is no gas flow gas flows out .