Endocrinology/VasopressinADH/ControlToWaterIntake/basic
| With water intake, the (red→blue) negative feedback decreases (the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of) vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH). |
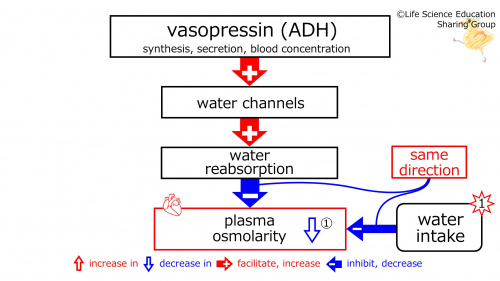
1st star (illustration): Subject had water. With water intake, plasma osmolarity decreases.(Synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of )vasopressin (ADH) (increases water channels. Water channels increase water reabsorption. Water reabsorption) decreases plasma osmolarity.
①(illustration): These are in the same direction (red).
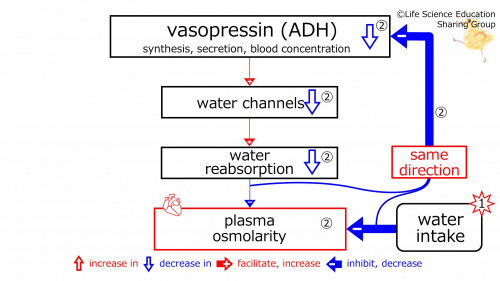
②(illustration): Since these are in the same direction (red), negative feedback decreases (blue) (synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of vasopressin (ADH).
With the decrease in (the synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of)vasopressin (ADH), (water channel-decreasing effect is strengthened, and water channels are decreased. With the increase in water channels, water reabsorption-decreasing effect is strengthened, and water absorption is decreased. With the decrease in water reaborption), plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect is strengthened.
Because of this control, the decreased plasma osmolarity decreases (towards that before water intake).
Namely, the initial change (the decrease in plasma osmolarity) decreases (blue downward unfilled arrow disappears).
Similar to cooler (function) being increased when room temperature is increased (winter), this also is red→blue negative feedback.
Challenge Quiz
Water intake increases decreases plasma osmolarity, and water reabsorption (through the water channels, which are increased by vasopressin, ADH) increases decreases plasma osmolarity. Since these effects are in the same opposite direction, negative feedback increases decreases (the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of) vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH).