Endocrinology/VasopressinADH/ControlToWaterIntake/basic
| With water intake, the (red→blue) negative feedback decreases (the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of) vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH). |
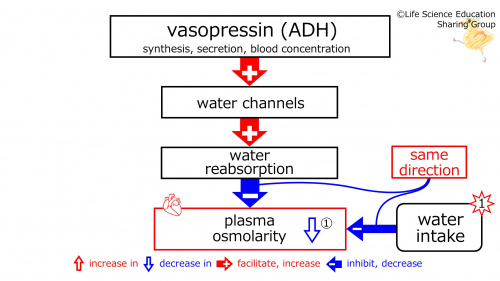
1st star (illustration): Subject sweated. With water intake, plasma osmolarity decreases.(Synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of )vasopressin (ADH) (increases water channels. Water channels increase water reabsorption. Water reabsorption) decreases plasma osmolarity.
①(illustration): These are in the same direction (red).
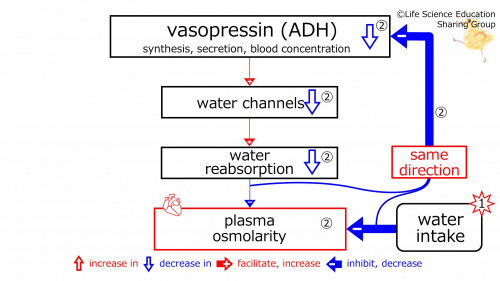
②(illustration): Since these are in the same direction (red), negative feedback decreases (blue) (synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of vasopressin (ADH).
With the decrease in (the synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of)vasopressin (ADH), (water channel-increasing effect is strengthened, and water channels are increased. With the increase in water channels, water reabsorption-increasing effect is strengthened, and water absorption is increased. With the increase in water reaborption), plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect is strengthened.
This decreases the number of water channels and the water reabsorption. The plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect of the water reabsorption becomes weaker. This will lead to a reverse in the decreased plasma osmolarity (diluted, hypotonic) produced by water intake, increasing it towards normal (baseline, isotonic) osmolarity.
Challenge Quiz
Water intake increases decreases plasma osmolarity, and water reabsorption (through the water channels, which are increased by vasopressin, ADH) increases decreases plasma osmolarity. Since these effects are in the same opposite direction, negative feedback increases decreases (the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of) vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH).