Endocrinology/VasopressinADH/SummaryOfEffect/basic
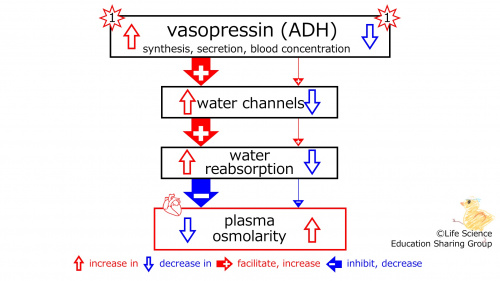
| With an increase/a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases/decreases, which increases/decreases the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity is decreased/increased. |
With an increase/a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases/decreases, which increases/decreases the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect of reabsorption increases/decreases, and the plasma osmolarity decreases (diluted, hypotonic)/increases (concentrated, hypertonic).
Challenge Quiz
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases decreases , which increases decreases the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity decreases (diluted, hypotonic).
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases decreases , which increases decreases the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity increases (concentrated, hypertonic).