Muscle/MuscleContraction/TheCrossbridgeCycle
The Crossbridge Cycle
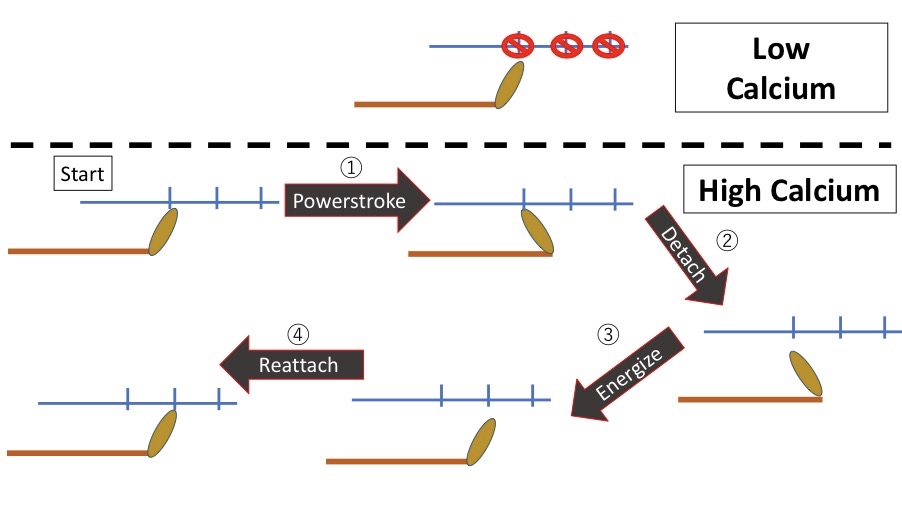
Low Calcium When there is low calcium the binding site is unavailable. The myosin head cannot bind to actin. The muscle is at rest.
High Calcium An increase in intracellular concentration will lead to the High Calcium state. In this state the binding sites on the thin filament are now available for the myosin head.
Start. When the intracellular calcium level rises the already-energized myosin head will bind to an available site on the thin filament. This forms the crossbridge.
①. Powerstroke. Once attached the energy within the myosin head will be used to perform the powerstroke. The myosin head moves on its hinge and pulls the thin filament with it.
②. Detach. At the end of the powerstroke ATP binds to the myosin head. This binding of ATP causes the myosin head to detach from the thin filament.
③. Energize. The ATPase on the myosin head hydrolyzes the ATP. This allows for the re-cocking of the myosin head and the storage of the energy that will be used for the next powerstroke.
④. Reattach. If calcium is still high the binding sites on actin are still available. The myosin head can bind to the thin filament forming the crossbridge. Note this will be to a binding site closer to the Z line than the first binding site.
Steps 1-4 will continue for as long as intracellular calcium is elevated and ATP is available.
Challenge Quiz
You must wait for the CORRECT! 正確!
<GIFT> //LEVEL:2 //RAND The binding of the myosin head to actin is prevented by the calcium levels being too {=low~high}
//LEVEL:2 //RAND An increase in {=calcium~sodium} in the {=intracellular~extracellular} fluid initiates muscle contraction.
//LEVEL:2 //RAND When the myosin head is bound to the thin filament it is called a crossbridge {=True~False}
//LEVEL:2 //RAND The myosin head derives its energy for the powerstroke {=before~after} biding to the thin filament.
//LEVEL:2 //RAND ATP binds to the myosin head {before~=after} the powerstroke.
//LEVEL:2
//RAND
The detachment of the myosin head from the thin filament requires {=ATP~calcium}
//LEVEL:2 //RAND After crossbridge detachment ATP is hydrolyzed {=True~False}
//LEVEL:2 //RAND If intracellular calcium remains {=high~low} the myosin head will be able to rebind to the thin filament at a site {further away~=closer to} the Z line.