Nerv06/introduction/autonomic ganglion
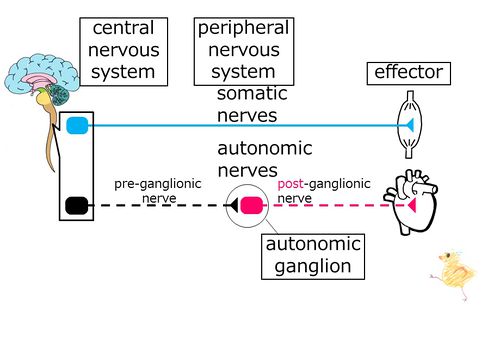
| The efferent fiber of the autonomic nervous system innervates the effector after forming a synapse at the autonomic ganglion. |
The (blue-colored) efferent fiber of the somatic nervous system innervates the effector directly after leaving the central nervous system. Meanwhile, in the autonomic nervous system (shown in dash lines), after the efferent fibers (shown in black dash line) leaves the central nervous system, it forms a synapse with a different (pink-colored) neuron outside of the central nervous system, and the fiber of that neuron (shown in pink dash line) innervates the effectors, such as internal organs. Such synapse of the autonomic nervous system, outside of the central nervous system, is called the autonomic ganglion. The (black) neuron, which left the central nervous system, is the neuron before the ganglion, and is thus called the pre-ganglionic neuron. The (pink) neuron, whose cell body is in the ganglion and innervates the effectors such as the internal organs, is the neuron after the ganglion, and is thus called the post-ganglionic neuron.
Challenge Quiz
In the somatic nervous system, there is a.are no synapse out of the central nervous system.
In the autonomic nervous system, there is a. are no synapse out of the central nervous system.
In the somatic.autonomic nervous system, there is a synapse out of the central nervous system.
In the somatic. autonomic nervous system, there are no synapse out of the central nervous system.