呼吸/respiratory cycle in English/Lung volume and pleural pressure
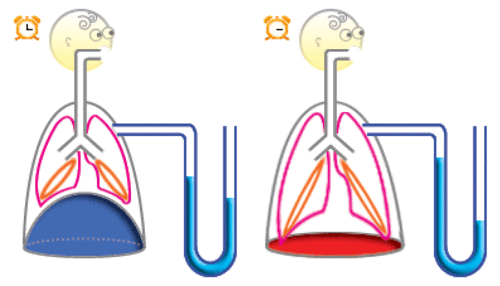
When the thoracic cavity increases in volume with inspiration, the negative pleural pressure becomes larger.
Inspiratory muscles, such as the diaphragm, contract, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. Because of the thin liquid film, the lung volume is also increased. Since this is in the opposite direction of the lung elasticity (note that the 'rubber bands' are further stretched), the negative pleural pressure becomes larger (note the blue pressure gauge).
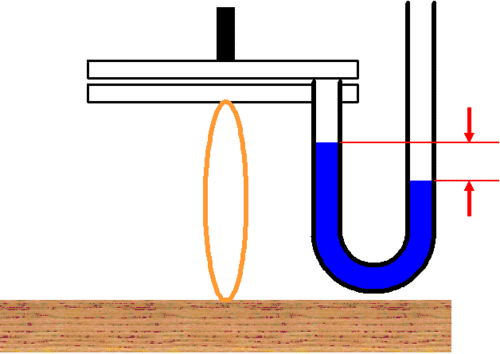
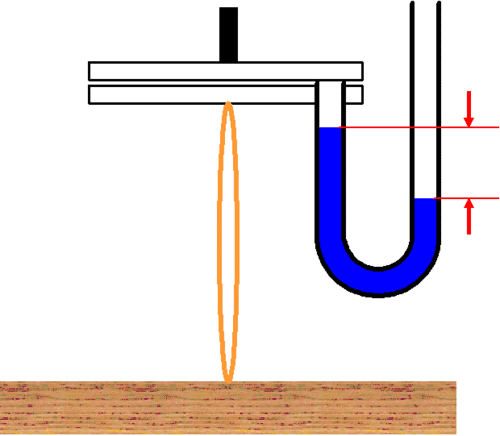
This is similar to: A rubber band is attached to a desk and the lower glass slide. With water inbetween, when the upper glass slide is lifted, pulling the rubber band lightly, the negative pressure inbetween is small, but
when the rubber band is pulled strongly, the negative pressure inbetween is large. Inspiration is like the latter situation.
| lung volume | min | max |
| inward elastic force of the lungs | min | max |
| negative pleural pressure | min | max |
(within one quiet respiratory cycle)
Challenge Quiz
When the thoracic cavity increases in volume during inspiration.~the positive.negative pleural pressure increases. decreases .
When the thoracic cavity decreases in volume during expiration.~the positive.negative pleural pressure increases.decreases .