SHolroydAtWeilCornellMedQatar/Urology/Kidney/Tubules/WaterReabsorption/EffectOfDecrease
| With the decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), the number of water channels decreases . |
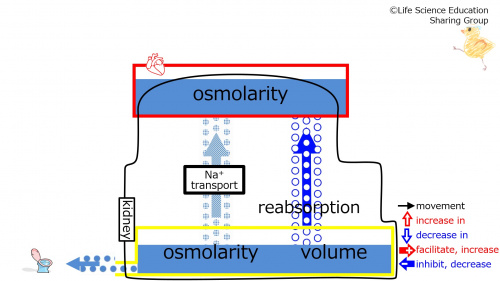
Prior to vasopressin (ADH) decreasing (at baseline), we will make the assumption that the subject is in homeostasis with normal plasma and urine osmolarities (isotonic) and volumes.
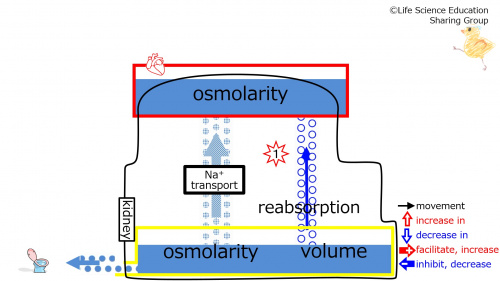
Step 1: Suppose that the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH) decreases.
Step 2: The water channel-increasing effect of vasopressin (ADH) decreases, thereby decreasing the number of water channels. This decreases the reabsorption of water by the kidney.
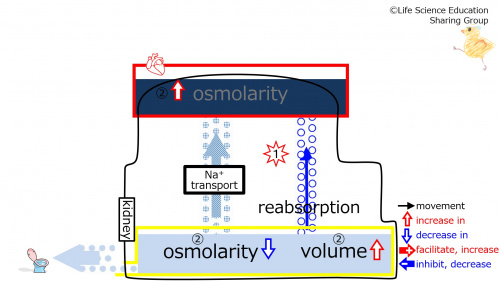
Step 3: The ratio of Na+ to water entering the plasma due to reabsorption increases. This increases plasma osmolarity (hypertonic). Because a higher ratio of Na+ to water leaves the tubule due to reabsorption, the fluid remaining in the tubule has a lower osmolarity (hypotonic). Also, with a decrease in water reabsorption, there is more water remaining in the tubule. Overall, the urine becomes less concentrated (hypotonic) and higher in volume.
Challenge Quiz
With a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), the number of water channels in the kidney increases decreases .
With a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), water reabsorption by the kidney increases decreases .
With a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine volume increases decreases .
With a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine osmolarity increases decreases .
With a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), plasma osmolarity increases decreases .
The effect of decreasing in vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH) is to contract female genital smooth muscle increase plasma osmolarity .
The effect of decreasing in vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH) is to increase decrease the plasma osmolarity .