「Endocrinology/HormonesWithoutMuchPituitaryRole/GlucagonAndInsuliln/Insulin/ControlBasic/Fasting」の版間の差分
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 1行目: | 1行目: | ||
{{Point|When blood glucose is decreased, negative feedback inhibits | {{Point|When blood glucose is decreased, negative feedback inhibits insulin (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration).}} | ||
[[メディア:insulin-fast.mp4|動画と音声での説明]] | [[メディア:insulin-fast.mp4|動画と音声での説明]] | ||
[[ファイル:InsulinBaselineJpn.jpg|left|500px]] | [[ファイル:InsulinBaselineJpn.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
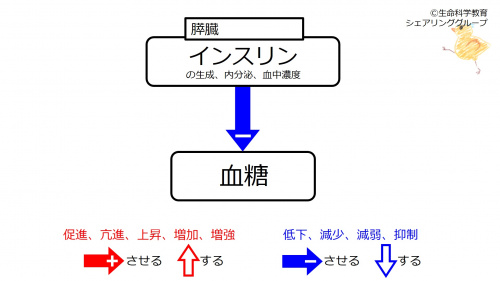
(Synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of) | (Synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of) insulin decreases blood glucose. Insulin has a certain (baseline) amount of synthesis, secretion, blood concentration, and blood glucose-increasing effect before fasting. | ||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
[[ファイル:insulin-fast.jpg|left|500px]] | [[ファイル:insulin-fast.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
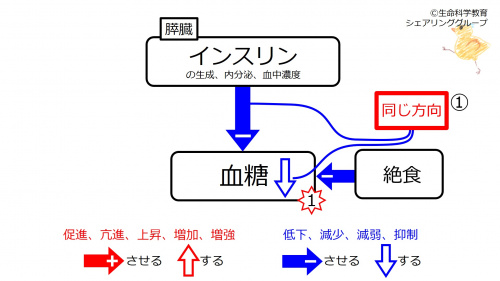
① Subject had fasted. Blood glucose is decreased due to the fasting. | ① Subject had fasted. Blood glucose is decreased due to the fasting. Insulin (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration) decreases blood glucose. These are in the <font color="#ff0000">same direction (red)</font>. | ||
| 14行目: | 14行目: | ||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
[[ファイル:グルカゴン・インスリン08.jpg|left|500px]] | [[ファイル:グルカゴン・インスリン08.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
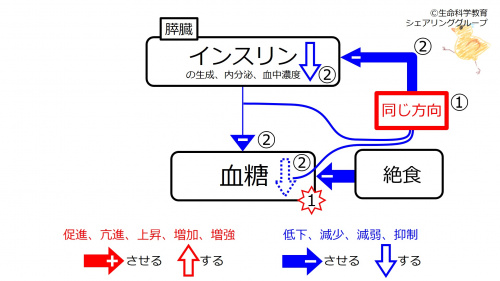
② Since these are in the <font color="#ff0000">same direction (red)</font>, negative feedback <font color="#00f">inhibits (blue)</font> | ② Since these are in the <font color="#ff0000">same direction (red)</font>, negative feedback <font color="#00f">inhibits (blue)</font> insulin (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration). Because of this, the blood glucose-decreasing effect of glucagon weakens, and the decrease in blood glucose (blue downward unfilled arrow) disappears (decreased blood glucose increases to the baseline). | ||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
| 25行目: | 25行目: | ||
//LEVEL:3 | //LEVEL:3 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
Blood glucose is {~increased~=decreased} due to the fasting, | Blood glucose is {~increased~=decreased} due to the fasting, insulin (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration {~increases~=decreases} blood glucose. Since these are in the {~=same direction~opposite direction}, negative feedback {~=inhibits~facilitates} insulin. Because of this, the initial transition dissapears and the blood glucose {~=increases~decreases} (towards the baseline). | ||
//LEVEL:2 | //LEVEL:2 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
When blood glucose is decreased, negative feedback {~facilitates~=inhibits} | When blood glucose is decreased, negative feedback {~facilitates~=inhibits} insulin (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration). | ||
</GIFT> | </GIFT> | ||
2023年8月9日 (水) 11:18時点における版
| When blood glucose is decreased, negative feedback inhibits insulin (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration). |
(Synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of) insulin decreases blood glucose. Insulin has a certain (baseline) amount of synthesis, secretion, blood concentration, and blood glucose-increasing effect before fasting.
① Subject had fasted. Blood glucose is decreased due to the fasting. Insulin (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration) decreases blood glucose. These are in the same direction (red).
② Since these are in the same direction (red), negative feedback inhibits (blue) insulin (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration). Because of this, the blood glucose-decreasing effect of glucagon weakens, and the decrease in blood glucose (blue downward unfilled arrow) disappears (decreased blood glucose increases to the baseline).
Like, when room temperature is decreased (winter), cooler (function) is decreased, this is also red→blue negative feedback.
Challenge Quiz
Blood glucose is increased decreased due to the fasting, insulin (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration increases decreases blood glucose. Since these are in the same direction opposite direction , negative feedback inhibits facilitates insulin. Because of this, the initial transition dissapears and the blood glucose increases decreases (towards the baseline).
When blood glucose is decreased, negative feedback facilitates inhibits insulin (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration).