「Nerve06/eyes and ears/pharyngotympanic (Eustachian) tube」の版間の差分
Soichi.Nakatake (トーク | 投稿記録) 編集の要約なし |
Soichi.Nakatake (トーク | 投稿記録) 編集の要約なし |
||
| 5行目: | 5行目: | ||
[[ファイル:01306.jpg|400px|left]] | [[ファイル:01306.jpg|400px|left]] | ||
The atmospheric pressure is lowered (shown in light blue) as an airplane or an elevator of a high building goes up. Since the tympanic cavity is a closed space, the pressure inside does not change from the 1st floor level (shown in dark blue). This results in pressure difference on both sides of the tympanic membrane, which becomes curved. Since the tympanic membrane also has sensory nerves. the curve causes uncomfortable or painful sensation making the subject want to 'pop' the ears. {{-}} | |||
[[ファイル:01307.jpg|400px|left]] | [[ファイル:01307.jpg|400px|left]] At this time, swallowing would cause the tube to open, releasing the high pressure to the pharynx. {{-}} | ||
[[ファイル:01308.jpg|400px|left]] | [[ファイル:01308.jpg|400px|left]] This cancels the pressure difference on both sides, and the curving, of the tympanic membrane. The ears are 'popped', and the uncomfortable sensation disappears. {{-}} | ||
| 22行目: | 24行目: | ||
//LEVEL:2 | //LEVEL:2 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
The pharyngotympanic (Eustachian) tube is {=opened.~closed} during swallowing. | |||
</GIFT> | </GIFT> | ||
2012年9月16日 (日) 17:09時点における版
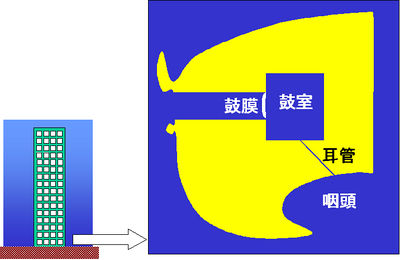
The pharyngotympanic (Eustachian) tube is connected to the pharynx and is usually closed, making the tympanic cavity a closed space. During swallowing or yawning, the tube is opened and the cavity becomes open to the outside, making the pressure inside the cavity equal to that of the atmosphere.
At the first floor of a building, the pressure of the cavity is equal to the atmospheric pressure at that level (shown in thick blue). Both the tube and cavity are closed.
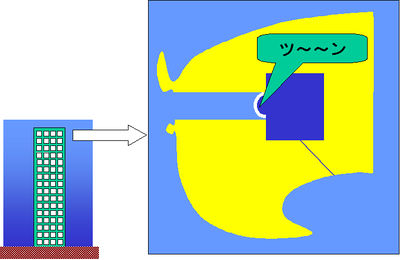
The atmospheric pressure is lowered (shown in light blue) as an airplane or an elevator of a high building goes up. Since the tympanic cavity is a closed space, the pressure inside does not change from the 1st floor level (shown in dark blue). This results in pressure difference on both sides of the tympanic membrane, which becomes curved. Since the tympanic membrane also has sensory nerves. the curve causes uncomfortable or painful sensation making the subject want to 'pop' the ears.
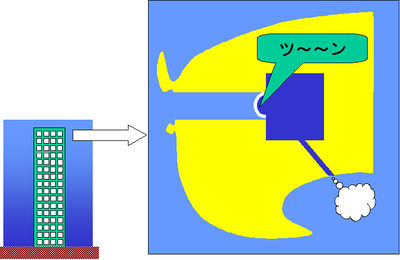
At this time, swallowing would cause the tube to open, releasing the high pressure to the pharynx.
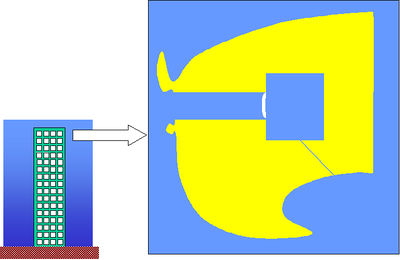
This cancels the pressure difference on both sides, and the curving, of the tympanic membrane. The ears are 'popped', and the uncomfortable sensation disappears.
Challenge Quiz
The pharyngotympanic (Eustachian) tube is opened. closed during swallowing.