「Muscle06/effect of intrafusal muscles」の版間の差分
ナビゲーションに移動
検索に移動
Soichi.Nakatake (トーク | 投稿記録) 編集の要約なし |
Soichi.Nakatake (トーク | 投稿記録) 編集の要約なし |
||
| 9行目: | 9行目: | ||
//LEVEL:4 | //LEVEL:4 | ||
//NO-RAND | //NO-RAND | ||
The intrafusal muscles are innervated by the {=gamma | The intrafusal muscles are innervated by the {=gamma.~alpha} motor neurons. | ||
//LEVEL:4 | //LEVEL:4 | ||
//NO-RAND | //NO-RAND | ||
The extrafusal muscles are innervated by the {~gamma | The extrafusal muscles are innervated by the {~gamma.=alpha} motor neurons. | ||
2012年9月27日 (木) 20:38時点における版
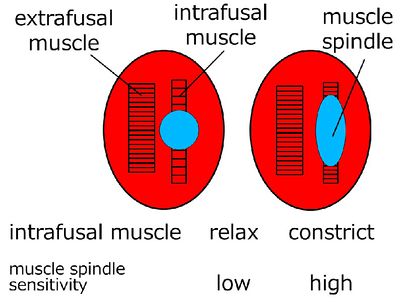
The intrafusal muscles locate on both ends of the muscle spindle. So, when the intrafusal muscles contract, the muscle spindle is stretched and sensitivity to further stretching is increased.
The extrafusal muscles are innervated by alpha motor neurons, and the intrafusal muscles innervated by the gamma motor neurons.
Challenge Quiz
1.
The intrafusal muscles are innervated by the gamma. alpha motor neurons.
2.
The extrafusal muscles are innervated by the gamma.alpha motor neurons.
3.
With contraction of the intrafusal muscles, the sensitivity of the muscle spindles increase. does not change very much. decrease .