「Nerve06/autonomic nervous system and synapses/catecholamine receptors」の版間の差分
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 3行目: | 3行目: | ||
[[ファイル:02538en.jpg|300px|left]] | [[ファイル:02538en.jpg|300px|left]] | ||
[[ファイル:02537en.jpg|300px]] | [[ファイル:02537en.jpg|300px]] | ||
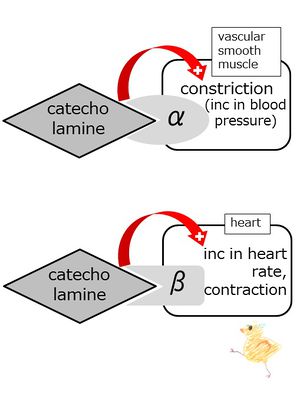
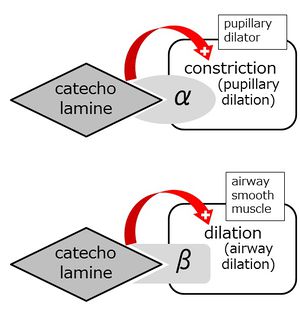
Alpha receptors: vascular smooth muslces (contraction, increase in blood pressure). gastrointestinal sphincters contraction. pupillary dilatator contraction. | Alpha receptors: vascular smooth muslces (contraction, increase in blood pressure). gastrointestinal sphincters contraction. pupillary dilatator contraction. | ||
2014年9月12日 (金) 17:44時点における版
There are two types, alpha receptors and beta receptors, of receptors for catecholamines. Depending on the organs innervated by the sympathetic nerves, the dominance of the alpha receptors and beta receptors differ.
 Alpha receptors: vascular smooth muslces (contraction, increase in blood pressure). gastrointestinal sphincters contraction. pupillary dilatator contraction.
Alpha receptors: vascular smooth muslces (contraction, increase in blood pressure). gastrointestinal sphincters contraction. pupillary dilatator contraction.
Beta receptors: cardiac muscles (increase in heart rate and contraction), relaxing of the airway smooth muscles.
Challenge Quiz
The catecholamine receptors in the vascular smooth muslces are mainly the alpha. beta receptors. When they are stimulated the blood pressure is lowered.elevated .
The catecholamine receptors in the heart muslces are mainly the alpha.beta receptors. When they are stimulated the cardiac contraction is fasciliated. inhibited and the heart rate is increased. decreased .
The catecholamine receptors in the airway smooth muslces are mainly the alpha.beta receptors. When they are stimulated the airway is dilated. constricted .