「SHolroydAtWeilCornellMedQatar/Endocrinology/VasopressinADH/EffectOfIncrease」の版間の差分
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| (3人の利用者による、間の35版が非表示) | |||
| 1行目: | 1行目: | ||
{{Point| With | {{Point| With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), the number of water channels and water reabsorption increase. These decrease plasma osmolarity and urine volume, and also increase urine osmolarity.}} | ||
[[メディア: | [[メディア:ADHeffectOfIncreaseEng.mp4|narrated video explanation]] | ||
<div class="avoid-page-break"> | <div class="avoid-page-break"> | ||
[[ファイル:ADHbaseline.jpg|left|500px]] | [[ファイル:ADHbaseline-Eng.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
[[メディア: | <!-- | ||
Prior to ADH increasing (at baseline), we will make the assumption that the subject is in homeostasis with normal plasma and urine osmolarities (isotonic) and | [[メディア:ADHbaseline-Eng.mp4|video prior to an increase in vasopressin (ADH)]]<br> | ||
--> | |||
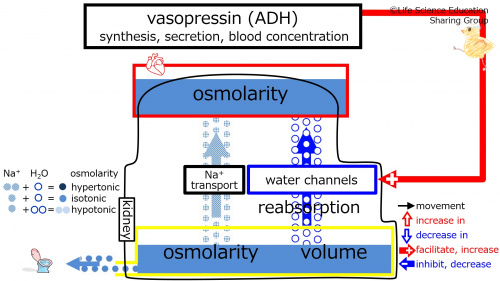
Prior to vasopressin (ADH) increasing (at baseline), we will make the assumption that the subject is in homeostasis with normal plasma and urine osmolarities (isotonic) and urine volume. | |||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="avoid-page-break"> | <div class="avoid-page-break"> | ||
[[ファイル: | [[ファイル:ADHEffectOfIncreasing-2Eng.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
[[メディア:ADHEffectOfIncreasing-2Eng.mp4|video just after | <!-- | ||
Step 1: Suppose that the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of ADH increases.<br> | [[メディア:ADHEffectOfIncreasing-2Eng.mp4|video just after an increase in vasopressin (ADH)]]<br> | ||
The water channel-increasing effect of ADH increases | --> | ||
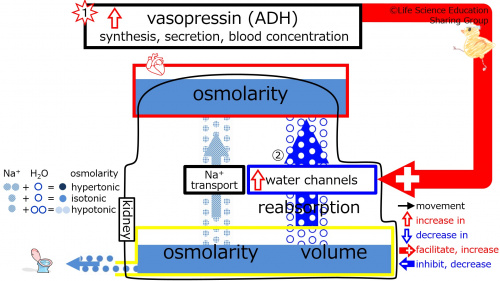
Step 1: Suppose that the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH) increases.<br> | |||
Step 2: The water channel-increasing effect of vasopressin (ADH) becomes stronger, which increases the number of water channels. This increases the water reabsorption from the tubule. | |||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
<div class="avoid-page-break"> | <div class="avoid-page-break"> | ||
[[ファイル: | [[ファイル:ADHEffectOfIncreasing-3Eng.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
[[メディア: | <!-- | ||
[[メディア:ADHEffectOfIncreasing-3Eng.mp4|video showing the changes in plasma and urine after the increase in vasopressin (ADH)]]<br> | |||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | --> | ||
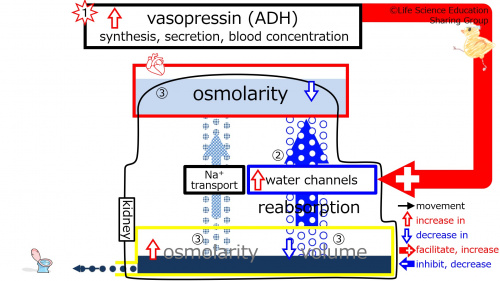
Step 3: With the increase in water reabsorption, diluted (hypotonic) solution enters the plasma. This decreases plasma osmolarity (diluted, hypotonic). Because diluted (hypotonic) solution leaves the tubule due to reabsorption, the fluid remaining in the tubule has an increased osmolarity (concentrated, hypertonic). Also, with the increase in water reabsorption, there is less water remaining in the tubule. Overall, the urine becomes concentrated and decreases in volume. <br style="clear:both;" /> | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
{{QuizTitle}} | {{QuizTitle}} | ||
<GIFT> | <GIFT> | ||
//LEVEL:2 | //LEVEL:2 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
With | With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), the number of water channels in the tubule {~=increases~decreases} . | ||
//LEVEL:2 | //LEVEL:2 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
With | With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), water reabsorption from the tubule {~=increases~decreases}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | //LEVEL:3 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
With | With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine volume {increases~=decreases}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | //LEVEL:3 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
With | With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine osmolarity {~=increases~decreases}. | ||
//LEVEL: | //LEVEL:2 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
With | With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), plasma osmolarity {increases~=decreases}. | ||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
The effect of increase in vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH) is {uterine smooth muscle contration~=a decrease in plasma osmolarity}. | |||
//LEVEL:3 | //LEVEL:3 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
The effect of increase in vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH) is {an increase~=a decrease} in plasma osmolarity. | |||
</GIFT> | </GIFT> | ||
2020年3月30日 (月) 10:49時点における最新版
| With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), the number of water channels and water reabsorption increase. These decrease plasma osmolarity and urine volume, and also increase urine osmolarity. |
Prior to vasopressin (ADH) increasing (at baseline), we will make the assumption that the subject is in homeostasis with normal plasma and urine osmolarities (isotonic) and urine volume.
Step 1: Suppose that the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH) increases.
Step 2: The water channel-increasing effect of vasopressin (ADH) becomes stronger, which increases the number of water channels. This increases the water reabsorption from the tubule.
Step 3: With the increase in water reabsorption, diluted (hypotonic) solution enters the plasma. This decreases plasma osmolarity (diluted, hypotonic). Because diluted (hypotonic) solution leaves the tubule due to reabsorption, the fluid remaining in the tubule has an increased osmolarity (concentrated, hypertonic). Also, with the increase in water reabsorption, there is less water remaining in the tubule. Overall, the urine becomes concentrated and decreases in volume.
Challenge Quiz
With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), the number of water channels in the tubule increases decreases .
With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), water reabsorption from the tubule increases decreases .
With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine volume increases decreases .
With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine osmolarity increases decreases .
With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), plasma osmolarity increases decreases .
The effect of increase in vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH) is uterine smooth muscle contration a decrease in plasma osmolarity .
The effect of increase in vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH) is an increase a decrease in plasma osmolarity.