「神経系/総論/膜電位の変化/挫滅症候群/高K血症の心筋への影響」の版間の差分
ナビゲーションに移動
検索に移動
(ページの作成: Category:nervous system {{Point|When a muscle is crushed, K<sup>+</sup> in blood is increased, and in cardiac muscle cells, diffusion of K<sup>+</sup> through K<sup>+</sup> c...) |
編集の要約なし |
||
| (同じ利用者による、間の12版が非表示) | |||
| 1行目: | 1行目: | ||
{{Point|筋肉が挫滅すると、カリウム( K<sup>+</sup>)が放出され、血中で上昇します。 チャンネル経由のカリウム( K<sup>+</sup>)の拡散は減少し、静止膜電位は減少し、不整脈が出現する。}} | |||
{{Point| | [[メディア:crush_syndrome_ja.mp4|動画と音声での説明]] | ||
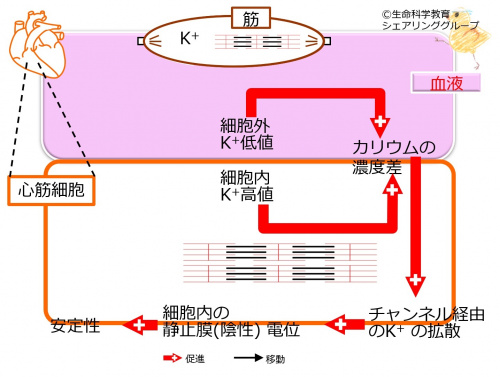
[[ファイル:CrushSyndromeJa-1.jpg|left|500px]]細胞内カリウム( K<sup>+</sup>)の高値と細胞外カリウム( K<sup>+</sup>)の低値とにより、細胞内外のカリウムの濃度差が生じ、これにより、チャンネル経由のカリウム( K<sup>+</sup>)の拡散が促進されます。 | |||
拡散が多いほど、細胞内の静止膜(陰性)電位が増大します。また、細胞内の静止膜電位が大きいほど、細胞は安定します。 | |||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | |||
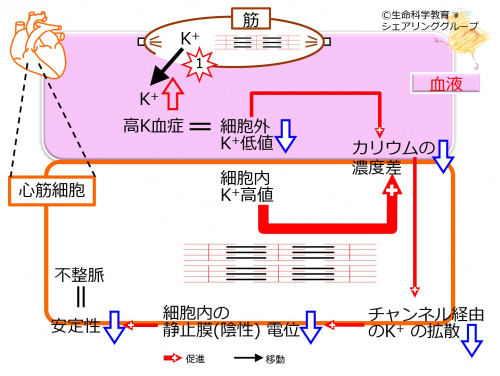
[[ファイル:crush_syndrome_ja.jpg|left|500px]] 地震で建物が崩壊し足が圧迫されるなどの場合、筋肉は挫滅し、カリウム( K<sup>+</sup>)が放出され、血中で上昇します。高カリウム血症では、細胞外カリウム( K<sup>+</sup>)が低値でなくなり、カリウムの細胞外と細胞内との差が減少します。 | |||
チャンネル経由のカリウム( K<sup>+</sup>)の拡散は減少し、 | |||
静止膜電位は減少します。これにより、心筋細胞の安定性も低下し、不整脈が出現します。 | |||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | |||
{{QuizTitle}} | {{QuizTitle}} | ||
<GIFT> | <GIFT> | ||
//LEVEL:3 | //LEVEL:3 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
筋肉が挫滅した場合、血中のカリウム( K<sup>+</sup>)が{=上昇~低下}し、心筋細胞では、チャンネル経由のカリウム( K<sup>+</sup>)の拡散は{=減少~増加}し、静止膜電位は{=減少~増加}する。これにより、心筋細胞の安定性も{~上昇~=低下}し、不整脈が出現する。 | |||
</gift> | </gift> | ||
2022年2月27日 (日) 23:51時点における最新版
POINT!
| 筋肉が挫滅すると、カリウム( K+)が放出され、血中で上昇します。 チャンネル経由のカリウム( K+)の拡散は減少し、静止膜電位は減少し、不整脈が出現する。 |
細胞内カリウム( K+)の高値と細胞外カリウム( K+)の低値とにより、細胞内外のカリウムの濃度差が生じ、これにより、チャンネル経由のカリウム( K+)の拡散が促進されます。
拡散が多いほど、細胞内の静止膜(陰性)電位が増大します。また、細胞内の静止膜電位が大きいほど、細胞は安定します。
地震で建物が崩壊し足が圧迫されるなどの場合、筋肉は挫滅し、カリウム( K+)が放出され、血中で上昇します。高カリウム血症では、細胞外カリウム( K+)が低値でなくなり、カリウムの細胞外と細胞内との差が減少します。
チャンネル経由のカリウム( K+)の拡散は減少し、
静止膜電位は減少します。これにより、心筋細胞の安定性も低下し、不整脈が出現します。
Challenge Quiz
1.
筋肉が挫滅した場合、血中のカリウム( K+)が 上昇 低下 し、心筋細胞では、チャンネル経由のカリウム( K+)の拡散は 減少 増加 し、静止膜電位は 減少 増加 する。これにより、心筋細胞の安定性も 上昇 低下 し、不整脈が出現する。