「Endocrinology/VasopressinADH/SummaryOfEffect/basic」の版間の差分
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 1行目: | 1行目: | ||
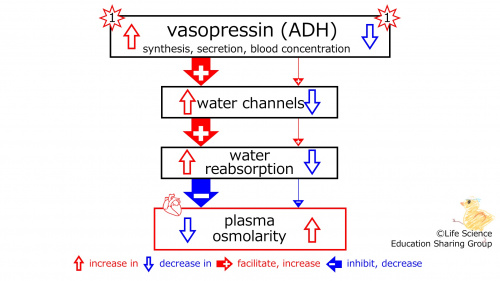
{{Point|With an increase/a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases/decreases, which increases/decreases the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity decreases/increases.}} | {{Point|With an increase/a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases/decreases, which increases/decreases the reabsorption of water (from the tubule). The plasma osmolarity decreases/increases.}} | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
[[メディア:heater-summer.mp4|動画と音声での説明]]<br> | [[メディア:heater-summer.mp4|動画と音声での説明]]<br> | ||
| 5行目: | 5行目: | ||
[[ファイル:ADHeffectSummaryBasic-ENG.jpg|left|500px]] | [[ファイル:ADHeffectSummaryBasic-ENG.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
With an increase/a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases/decreases, which increases/decreases the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect of reabsorption becomes stronger/weaker, and the plasma osmolarity decreases (diluted, hypotonic)/increases (concentrated, hypertonic). | With an increase/a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases/decreases, which increases/decreases the reabsorption of water (from the tubule). The plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect of reabsorption becomes stronger/weaker, and the plasma osmolarity decreases (diluted, hypotonic)/increases (concentrated, hypertonic). | ||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
| 12行目: | 12行目: | ||
//LEVEL:3 | //LEVEL:3 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
With {~=an increase~a decrease} in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) {~=increases~decreases}, which {~=increases~decreases} the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity decreases (diluted, hypotonic). | With {~=an increase~a decrease} in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) {~=increases~decreases}, which {~=increases~decreases} the reabsorption of water (from the tubule). The plasma osmolarity decreases (diluted, hypotonic). | ||
//LEVEL:3 | //LEVEL:3 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
With {~an increase~=a decrease} in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) {~increases~=decreases}, which {~increases~=decreases} the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity increases (concentrated, hypertonic). | With {~an increase~=a decrease} in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) {~increases~=decreases}, which {~increases~=decreases} the reabsorption of water (from the tubule). The plasma osmolarity increases (concentrated, hypertonic). | ||
</GIFT> | </GIFT> | ||
2020年3月15日 (日) 07:01時点における版
| With an increase/a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases/decreases, which increases/decreases the reabsorption of water (from the tubule). The plasma osmolarity decreases/increases. |
With an increase/a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases/decreases, which increases/decreases the reabsorption of water (from the tubule). The plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect of reabsorption becomes stronger/weaker, and the plasma osmolarity decreases (diluted, hypotonic)/increases (concentrated, hypertonic).
Challenge Quiz
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases decreases , which increases decreases the reabsorption of water (from the tubule). The plasma osmolarity decreases (diluted, hypotonic).
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases decreases , which increases decreases the reabsorption of water (from the tubule). The plasma osmolarity increases (concentrated, hypertonic).