「SHolroydAtWeilCornellMedQatar/Endocrinology/VasopressinADH/EffectSummary」の版間の差分
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 27行目: | 27行目: | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
With {~=an increase~a decrease} in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), plasma osmolarity decreases. | With {~=an increase~a decrease} in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), plasma osmolarity decreases. | ||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
With {~an increase~=a decrease} in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), the number of water channels in the tubule decreases. | |||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
With {~an increase~=a decrease} in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), water reabsorption from the tubule decreases. | |||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
With {~an increase~=a decrease} in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine volume increases. | |||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
With {~an increase~=a decrease} in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine osmolarity decreases. | |||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
With {~an increase~=a decrease} in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), plasma osmolarity increases. | |||
</GIFT> | </GIFT> | ||
2020年3月12日 (木) 23:23時点における版
Challenge Quiz
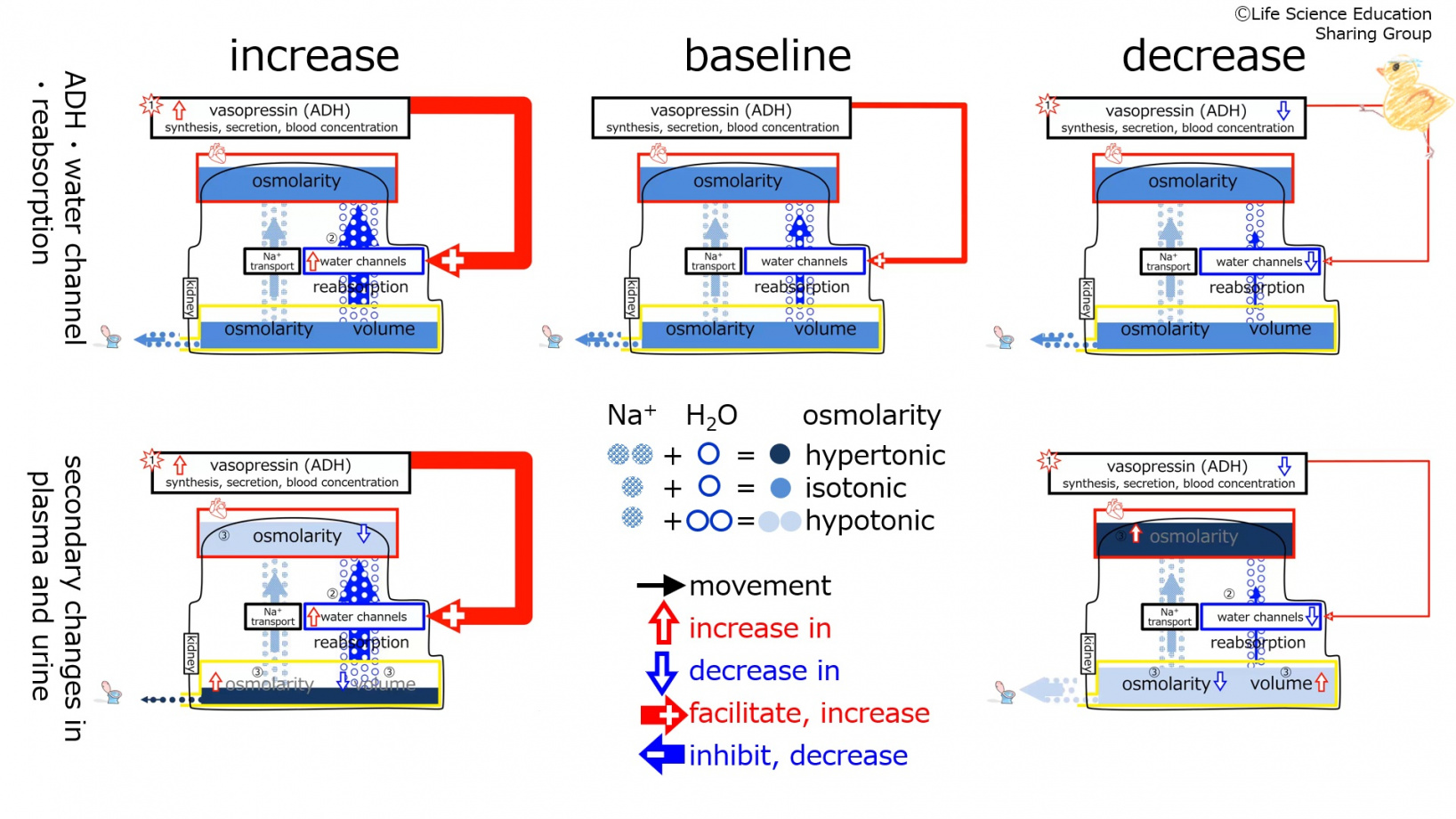
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), the number of water channels in the tubule increases.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), water reabsorption from the tubule increases.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine volume decreases.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine osmolarity increases.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), plasma osmolarity decreases.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), the number of water channels in the tubule decreases.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), water reabsorption from the tubule decreases.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine volume increases.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine osmolarity decreases.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), plasma osmolarity increases.