「Endocrinology/VasopressinADH/EffectOfIncrease/basic」の版間の差分
ナビゲーションに移動
検索に移動
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 5行目: | 5行目: | ||
[[ファイル:IncreasedADHbasic-ENG.jpg|left|500px]] | [[ファイル:IncreasedADHbasic-ENG.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
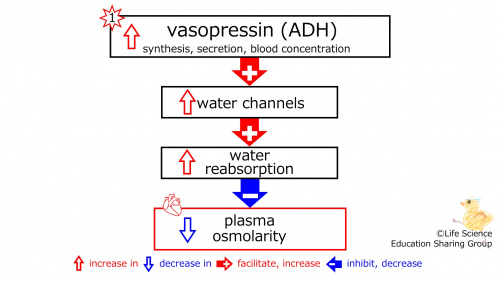
With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases, which increases the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect of reabsorption increases, and the plasma osmolarity decreases ( | With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases, which increases the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect of reabsorption increases, and the plasma osmolarity decreases (diluted, hypotonic). | ||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
2020年2月8日 (土) 09:29時点における版
POINT!
| With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases, which increases the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity is decreased. |
With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases, which increases the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect of reabsorption increases, and the plasma osmolarity decreases (diluted, hypotonic).
Challenge Quiz
1.
With an increase in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (ADH), the number of water channels (in the tubule) increases decreases , which increases decreases the reabsorption of water. The plasma osmolarity increases decreases .