「Endocrinology/CaHomeostasis/IntroToCaHomeostasis」の版間の差分
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 5行目: | 5行目: | ||
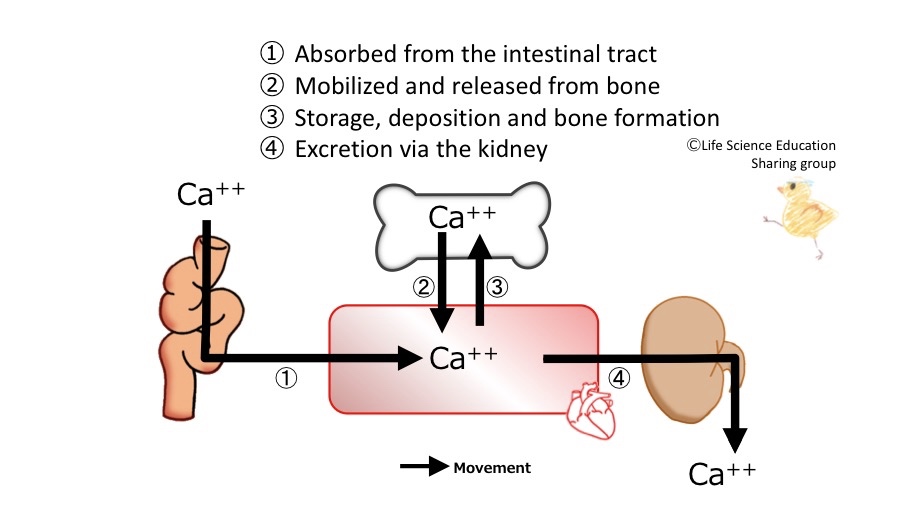
Calcium in the diet is absorbed from the small intestine into the blood (1). Most calcium in the body is stored in the bones. This calcium store can be mobilized leading to the release of calcium into the blood. This is defined as “bone resorption”. This weakens the bone (2). The movement of calcium from the blood to the bone is known as deposition and storage. This strengthens the bone (3). Most calcium is removed from the body through excretion by the kidneys (4). | Calcium in the diet is absorbed from the small intestine into the blood (1). Most calcium in the body is stored in the bones. This calcium store can be mobilized leading to the release of calcium into the blood. This is defined as “bone resorption”. This weakens the bone (2). The movement of calcium from the blood to the bone is known as deposition and storage. This strengthens the bone (3). Most calcium is removed from the body through excretion by the kidneys (4). | ||
{{QuizTitle}} | |||
You must wait for the CORRECT! 正確! | |||
<GIFT> | |||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
When calcium is absorbed by the small intestine, blood calcium concentration {~=increases~decreases}. | |||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
The greatest store of calcium in the body is the {~intestinal tract~=bones~blood~kidneys}. | |||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
The mobilization of the calcium store in the bone will produce a {~=increase~decrease} in blood calcium concentration. | |||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
When calcium is released from bone, blood calcium concentration {~=increases~decreases}. | |||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
If there is bone resorption, blood calcium concentration {~=increases~decreases}. | |||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
If there is bone deposition, blood calcium concentration {~increases~=decreases}. | |||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
Storage of calcium in bone will produce a {~increase~=decrease} in blood calcium concentration. | |||
//LEVEL:2 | |||
//RAND | |||
Excretion of calcium by the kidney will produce a {~increase~=decrease} in blood calcium concentration. | |||
2019年5月28日 (火) 19:17時点における版
Calcium Homeostasis
Calcium in the diet is absorbed from the small intestine into the blood (1). Most calcium in the body is stored in the bones. This calcium store can be mobilized leading to the release of calcium into the blood. This is defined as “bone resorption”. This weakens the bone (2). The movement of calcium from the blood to the bone is known as deposition and storage. This strengthens the bone (3). Most calcium is removed from the body through excretion by the kidneys (4).
Challenge Quiz
You must wait for the CORRECT! 正確!
<GIFT> //LEVEL:2 //RAND When calcium is absorbed by the small intestine, blood calcium concentration {~=increases~decreases}.
//LEVEL:2 //RAND The greatest store of calcium in the body is the {~intestinal tract~=bones~blood~kidneys}.
//LEVEL:2 //RAND The mobilization of the calcium store in the bone will produce a {~=increase~decrease} in blood calcium concentration.
//LEVEL:2
//RAND
When calcium is released from bone, blood calcium concentration {~=increases~decreases}.
//LEVEL:2
//RAND
If there is bone resorption, blood calcium concentration {~=increases~decreases}.
//LEVEL:2
//RAND
If there is bone deposition, blood calcium concentration {~increases~=decreases}.
//LEVEL:2
//RAND
Storage of calcium in bone will produce a {~increase~=decrease} in blood calcium concentration.
//LEVEL:2
//RAND
Excretion of calcium by the kidney will produce a {~increase~=decrease} in blood calcium concentration.