「2014特論英語テスト」の版間の差分
(ページの作成:「<gift> In energy metabolism, {~atom~=bonds between atoms} of nutrients are removed, and the nutrient is degenerated. With tissue (cellular) respiration, the oxygen in th...」) |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 1行目: | 1行目: | ||
<gift> | <gift> | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
In energy metabolism, {~atom~=bonds between atoms} of nutrients are removed, and the nutrient is degenerated. | In energy metabolism, {~atom~=bonds between atoms} of nutrients are removed, and the nutrient is degenerated. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
With tissue (cellular) respiration, the oxygen in the blood {~=decreases~increases}. | With tissue (cellular) respiration, the oxygen in the blood {~=decreases~increases}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
The * mark in the illustration indicates {~=energy removal from nutrient~nutrient degeneration~facilitation of energy metabolism by oxygen~contraction of contractile protein in muscle~oxyten intake by cell}. | The * mark in the illustration indicates {~=energy removal from nutrient~nutrient degeneration~facilitation of energy metabolism by oxygen~contraction of contractile protein in muscle~oxyten intake by cell}. | ||
[[画像:クイズ1.jpg|300px|right]] | [[画像:クイズ1.jpg|300px|right]] | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
The * mark in the illustration indicates {~energy removal from nutrient~=nutrient degeneration~facilitation of energy metabolism by oxygen~contraction of contractile protein in muscle~oxyten intake by cell}. | The * mark in the illustration indicates {~energy removal from nutrient~=nutrient degeneration~facilitation of energy metabolism by oxygen~contraction of contractile protein in muscle~oxyten intake by cell}. | ||
[[画像:クイズ2.jpg|300px|right]] | [[画像:クイズ2.jpg|300px|right]] | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
The chemical energy of a nutrient is in the {~atom~=bonds between atoms}. | The chemical energy of a nutrient is in the {~atom~=bonds between atoms}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
In energy metabolism, {~nutrient~oxygen~=carbon dioxide~=water} (is)are synthesized and excreted from the cell. | In energy metabolism, {~nutrient~oxygen~=carbon dioxide~=water} (is)are synthesized and excreted from the cell. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
With oxygen, the efficiency of energy metabolism is {~=high~low}. | With oxygen, the efficiency of energy metabolism is {~=high~low}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
The * mark in the illustration indicates that in the aerobic metabolism, compared to the anaerobic metabolism {~=more ATP synthesis from certain amount of nutrient~takes more time~less energy is left in the metabolite~less ATP synthesis from certain amount of nutrient~takes less time~more energy is left in the metabolite}. | The * mark in the illustration indicates that in the aerobic metabolism, compared to the anaerobic metabolism {~=more ATP synthesis from certain amount of nutrient~takes more time~less energy is left in the metabolite~less ATP synthesis from certain amount of nutrient~takes less time~more energy is left in the metabolite}. | ||
[[画像:04117.jpg|300px|right]] | [[画像:04117.jpg|300px|right]] | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
When jogging long distance, the main source of ATP synthesis is the {~anaerobic~=aerobic} metabolism. | When jogging long distance, the main source of ATP synthesis is the {~anaerobic~=aerobic} metabolism. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
The actual high-energy substance utilized by actin and myosin in myocytes are {~glucose~=ATP~ADP}. | The actual high-energy substance utilized by actin and myosin in myocytes are {~glucose~=ATP~ADP}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
In aerobic metabolism, compared to anaerobic metabolism, the chemical energy in the metabolites are {~larger~=smaller}. | In aerobic metabolism, compared to anaerobic metabolism, the chemical energy in the metabolites are {~larger~=smaller}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
In anaerobic metabolism, compared to aerobic metabolism, the amount of ATP that can be synthesized in a (short) period of time is {~=larger~smaller}. | In anaerobic metabolism, compared to aerobic metabolism, the amount of ATP that can be synthesized in a (short) period of time is {~=larger~smaller}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
Aerobic metabolism, compared to anaerobic metabolism, takes places {~earlier~=later}. | Aerobic metabolism, compared to anaerobic metabolism, takes places {~earlier~=later}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
During ATP synthesis, nutrients are {~synthesized~=degraded}. | During ATP synthesis, nutrients are {~synthesized~=degraded}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
The * mark of the illustration indicates {~citric acid (Krebs, TCA)cycle~ATP synthase~β oxidation~glycolysis~=electron transport system}である。 | The * mark of the illustration indicates {~citric acid (Krebs, TCA)cycle~ATP synthase~β oxidation~glycolysis~=electron transport system}である。 | ||
[[画像:クイズ_電子伝達系.jpg|300px|right]] | [[画像:クイズ_電子伝達系.jpg|300px|right]] | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
In energy metabolism, {~nutrient~oxygen~=carbon dioxide~=water} (is)are synthesized and excreted from the cell. | In energy metabolism, {~nutrient~oxygen~=carbon dioxide~=water} (is)are synthesized and excreted from the cell. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
The * mark in the illustration indicates {~energy removal from nutrient~=nutrient degeneration~facilitation of energy metabolism by oxygen~contraction of contractile protein in muscle~oxyten intake by cell}. | The * mark in the illustration indicates {~energy removal from nutrient~=nutrient degeneration~facilitation of energy metabolism by oxygen~contraction of contractile protein in muscle~oxyten intake by cell}. | ||
[[画像:クイズ2.jpg|300px|right]] | [[画像:クイズ2.jpg|300px|right]] | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
The energy directly used during cell activity are those in {~=ATP~ADP~glucose}. | The energy directly used during cell activity are those in {~=ATP~ADP~glucose}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
By the action of the electron transport system, the concentration of protons (H<sup>+</sup>) outside of the inner membrane of mitocondria are {~=increased~decreased}. | By the action of the electron transport system, the concentration of protons (H<sup>+</sup>) outside of the inner membrane of mitocondria are {~=increased~decreased}. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | |||
//RAND | |||
Among the choices, ATP synthase synthetize mostly {~hydrogen atoms~=ATP~concentration gradient of hydrogen ions (H<sup>+</sup>) or protons}. | Among the choices, ATP synthase synthetize mostly {~hydrogen atoms~=ATP~concentration gradient of hydrogen ions (H<sup>+</sup>) or protons}. | ||
</gift> | </gift> | ||
2014年12月4日 (木) 19:32時点における版
In energy metabolism, atom bonds between atoms of nutrients are removed, and the nutrient is degenerated.
With tissue (cellular) respiration, the oxygen in the blood decreases increases .
The * mark in the illustration indicates energy removal from nutrient nutrient degeneration facilitation of energy metabolism by oxygen contraction of contractile protein in muscle oxyten intake by cell .
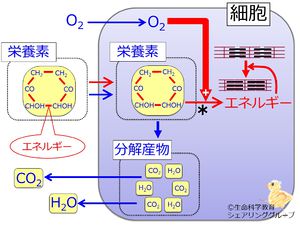
The * mark in the illustration indicates energy removal from nutrient nutrient degeneration facilitation of energy metabolism by oxygen contraction of contractile protein in muscle oxyten intake by cell .
The chemical energy of a nutrient is in the atom bonds between atoms .
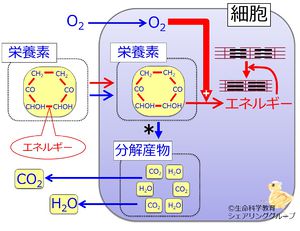
In energy metabolism, nutrient oxygen carbon dioxide water (is)are synthesized and excreted from the cell.
With oxygen, the efficiency of energy metabolism is high low .
The * mark in the illustration indicates that in the aerobic metabolism, compared to the anaerobic metabolism more ATP synthesis from certain amount of nutrient takes more time less energy is left in the metabolite less ATP synthesis from certain amount of nutrient takes less time more energy is left in the metabolite .
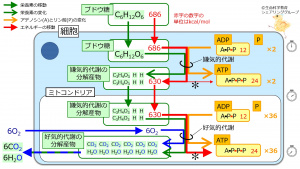
When jogging long distance, the main source of ATP synthesis is the anaerobic aerobic metabolism.
The actual high-energy substance utilized by actin and myosin in myocytes are glucose ATP ADP .
In aerobic metabolism, compared to anaerobic metabolism, the chemical energy in the metabolites are larger smaller .
In anaerobic metabolism, compared to aerobic metabolism, the amount of ATP that can be synthesized in a (short) period of time is larger smaller .
Aerobic metabolism, compared to anaerobic metabolism, takes places earlier later .
During ATP synthesis, nutrients are synthesized degraded .
The * mark of the illustration indicates citric acid (Krebs, TCA)cycle ATP synthase β oxidation glycolysis electron transport system である。
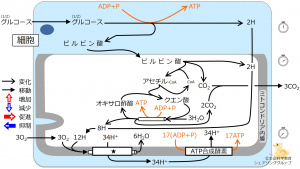
In energy metabolism, nutrient oxygen carbon dioxide water (is)are synthesized and excreted from the cell.
The * mark in the illustration indicates energy removal from nutrient nutrient degeneration facilitation of energy metabolism by oxygen contraction of contractile protein in muscle oxyten intake by cell .

The energy directly used during cell activity are those in ATP ADP glucose .
By the action of the electron transport system, the concentration of protons (H+) outside of the inner membrane of mitocondria are increased decreased .
Among the choices, ATP synthase synthetize mostly hydrogen atoms ATP concentration gradient of hydrogen ions (H+) or protons .