「Nervous system/overview of neurons/Channels/membrane potential/effect on diffusion」の版間の差分
ナビゲーションに移動
検索に移動
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 10行目: | 10行目: | ||
//LEVEL:3 | //LEVEL:3 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
The electric force of the negative intracellular membrane potential moves potassium (K<sup>+</sup>) {=from outside to inside | The electric force of the negative intracellular membrane potential moves potassium (K<sup>+</sup>) {=from outside to inside~from inside to outside} of the cell. | ||
//LEVEL:3 | //LEVEL:3 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
When the potassium (K<sup>+</sup>) channel is open, the diffusion continues until there is no difference in concentration between inside and outside the cell. {~true | When the potassium (K<sup>+</sup>) channel is open, the diffusion continues until there is no difference in concentration between inside and outside the cell. {~true~=false} | ||
</GIFT> | </GIFT> | ||
2014年11月18日 (火) 22:15時点における版
POINT!
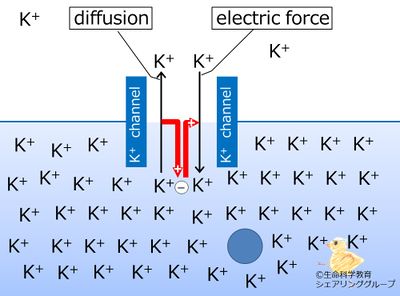
| The electric force of the negative intracellular membrane potential moves potassium (K+) from outside to inside of the cell. |
video: Flash(Win, Mac) / MP4(iPad)
When the potassium channels open and potassium ions diffuse OUT of the cell, the intracellular potential becomes negative. Because of this negative potential, part of the diffused ions are pulled back into the cell.
Challenge Quiz
1.
The electric force of the negative intracellular membrane potential moves potassium (K+) from outside to inside from inside to outside of the cell.
2.
When the potassium (K+) channel is open, the diffusion continues until there is no difference in concentration between inside and outside the cell. true false