「Nervous system/overview of neurons/Crush syndrome/effect of hyperkalemia on cardiac muscle」の版間の差分
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 1行目: | 1行目: | ||
[[Category:nervous system]] | [[Category:nervous system]] | ||
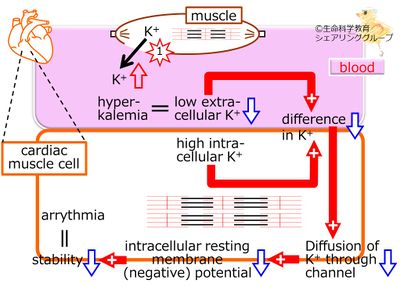
{{Point|When a muscle is crushed, K<sup>+</sup> in blood is increased, and in cardiac muscle cells, diffusion of K<sup>+</sup> through K<sup>+</sup> channel is less, resting membrane potential is less, stability of the cell is less, causing arrythmia.}} | {{Point|When a muscle is crushed, K<sup>+</sup> in blood is increased, and in cardiac muscle cells, diffusion of K<sup>+</sup> through K<sup>+</sup> channel is less, resting membrane potential is less, stability of the cell is less, causing arrythmia.}} | ||
video: [[メディア:crush_synd.swf|Flash]](Win, Mac) / [[メディア:crush_synd.m4v|MP4]](iPad) | |||
[[ファイル:Crush synd.jpg|alt=Crush synd.jpg|left|400px]] | |||
Both the high intra-cellular potassium (K+) and low extra-cellular potassium (K+) bring about the difference, which is the driving force of the diffusion of potassium ion (K+) through channel. | |||
With more diffusion, the intracellular resting membrane negative potential increases, and with more intracellular resting membrane potential, the cell becomes more stable | |||
When the legs are compressed for a long time, such as in earthquake-destroyed buildings, a muscle is crushed, <potassium (K+)> is released and then increased in the blood. Hyperkalemia means extracellular potassium is NOT as low, which also means that the difference between extra- and intra- cellular potassium (K+) is less. | |||
There will be less diffusion of K+ through the K+ channel, resting membrane potential decreases, and the stability of the cardiac muscle cell, decreases, causing arrhythmia. | |||
{{QuizTitle}} | {{QuizTitle}} | ||
<GIFT> | <GIFT> | ||
2014年6月6日 (金) 09:27時点における版
| When a muscle is crushed, K+ in blood is increased, and in cardiac muscle cells, diffusion of K+ through K+ channel is less, resting membrane potential is less, stability of the cell is less, causing arrythmia. |
video: Flash(Win, Mac) / MP4(iPad)
Both the high intra-cellular potassium (K+) and low extra-cellular potassium (K+) bring about the difference, which is the driving force of the diffusion of potassium ion (K+) through channel. With more diffusion, the intracellular resting membrane negative potential increases, and with more intracellular resting membrane potential, the cell becomes more stable
When the legs are compressed for a long time, such as in earthquake-destroyed buildings, a muscle is crushed, <potassium (K+)> is released and then increased in the blood. Hyperkalemia means extracellular potassium is NOT as low, which also means that the difference between extra- and intra- cellular potassium (K+) is less. There will be less diffusion of K+ through the K+ channel, resting membrane potential decreases, and the stability of the cardiac muscle cell, decreases, causing arrhythmia.
Challenge Quiz
When a muscle is crushed, K+ in blood is increased. decreased , and in cardiac muscle cells, diffusion of K+ through K+ channel is less. more , resting membrane potential is less. more , stability of the cell is less. more , causing arrythmia.