「Nervous system/overview of neurons/Channels/membrane potential/effect on diffusion」の版間の差分
ナビゲーションに移動
検索に移動
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 3行目: | 3行目: | ||
video: [[メディア:Potential2diffusion.swf|Flash]](Win, Mac) / [[メディア:Potential2diffusion.m4v|MP4]](iPad) | video: [[メディア:Potential2diffusion.swf|Flash]](Win, Mac) / [[メディア:Potential2diffusion.m4v|MP4]](iPad) | ||
[[ファイル:potential2diffusion.jpg|alt=potential2diffusion.jpg|left|400px]] | [[ファイル:potential2diffusion.jpg|alt=potential2diffusion.jpg|left|400px]] | ||
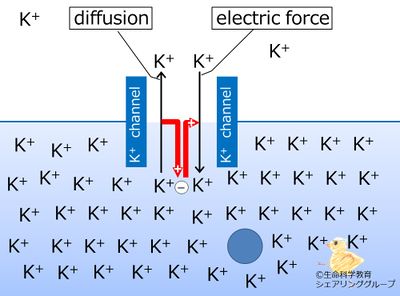
When the potassium channels open and potassium ions diffuse OUT of the cell, the intracellular potential becomes negative. | |||
Due to this negative potential , some of the diffused ions are pulled back into the cell. | |||
{{QuizTitle}} | {{QuizTitle}} | ||
<GIFT> | <GIFT> | ||
2014年5月29日 (木) 14:50時点における版
POINT!
| The electric force of the negative intracellular membrane potential moves potassium (K+) from outside to inside of the cell. |
video: Flash(Win, Mac) / MP4(iPad)
When the potassium channels open and potassium ions diffuse OUT of the cell, the intracellular potential becomes negative. Due to this negative potential , some of the diffused ions are pulled back into the cell.
Challenge Quiz
1.
The electric force of the negative intracellular membrane potential moves potassium (K+) from outside to inside. from inside to outside of the cell.
When the potassium (K+) channel is open, the diffusion continues until there is no difference in concentration between inside and outside the cell. true.false