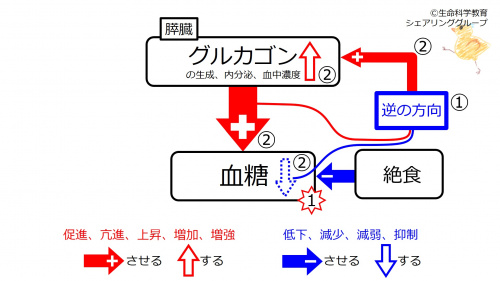
| When blood glucose is decreased, negative feedback facilitates glucagon (synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood). |
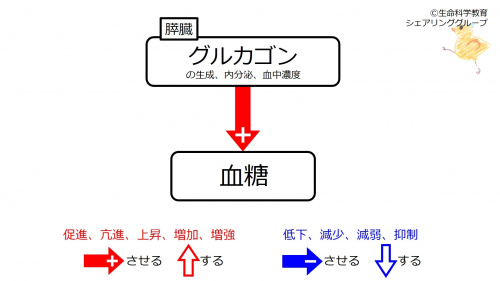
(Synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of) glucagon increases blood glucose. Before fast, glucagon has certain levels of synthesis, secretion, concentration in blood, and blood glucose-increasing effect.
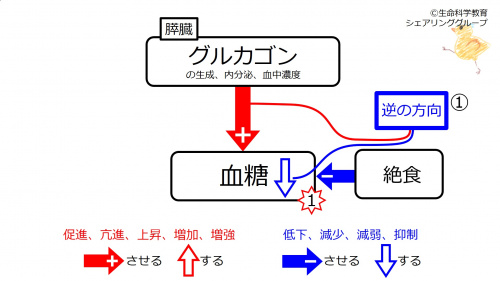
① Subject had fasted. Blood glucose is decreased due to the fasting. Glucacon (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration) increases blood glucose. These are in the opposite direction (blue).
② Since these are in the opposite direction (blue), negative feedback facilitates (red) glucagon (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration). Because of this, the blood glucose-increasing effect of glucagon strengthens, and the decrease in blood glucose (blue downward unfilled arrow) disappears (decreased blood glucose increases to the baseline).
Like, when room temperature is decreased (winter), heater (function) is increased, this also is blue→red negative feedback.
Challenge Quiz
When blood glucose is decreased, negative feedback inhibits facilitates glucagon (synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration).