検索結果
Challenge Quiz
1.
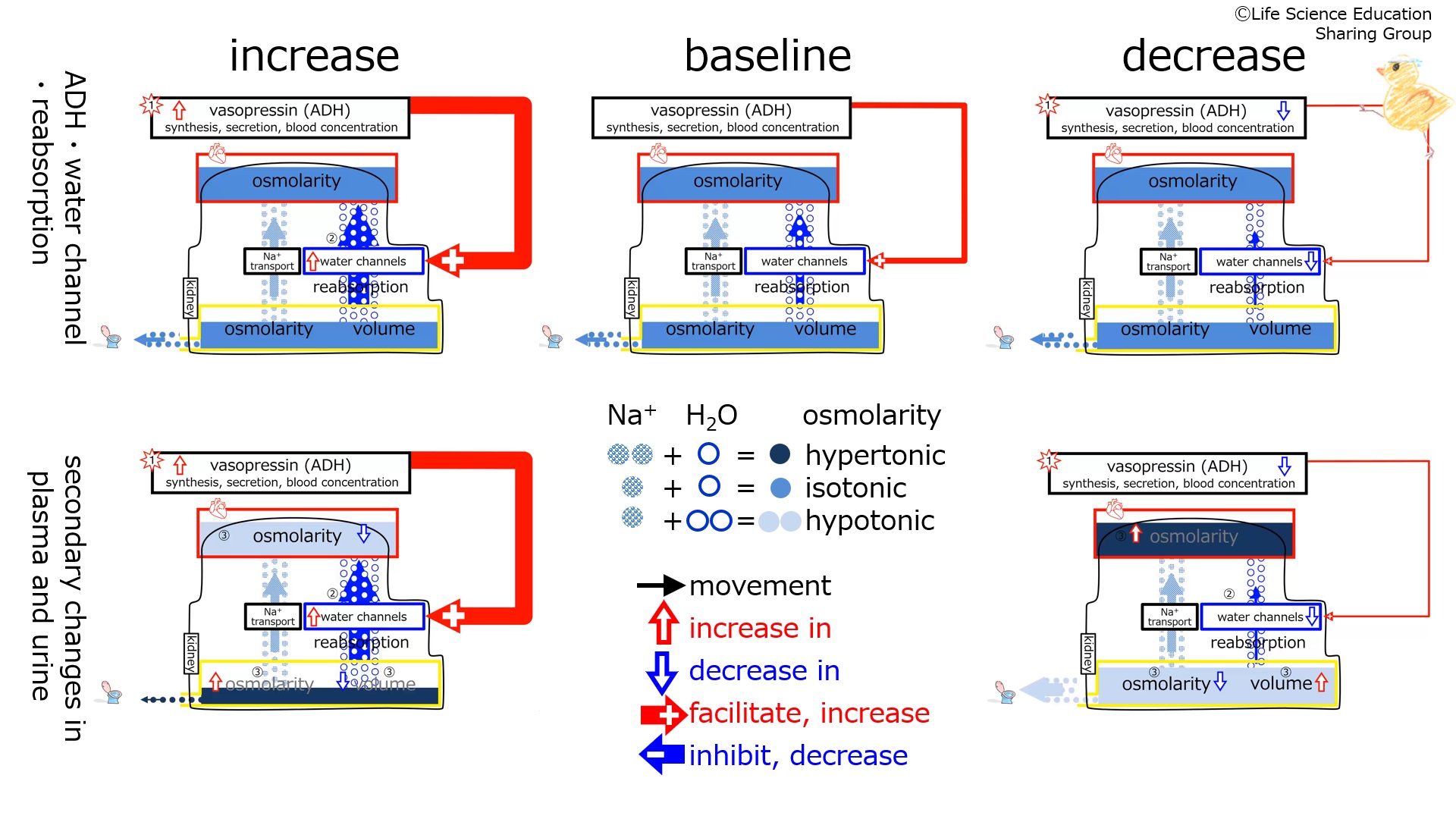
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), the number of water channels in the tubule increases.
2.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), water reabsorption from the tubule increases.
3.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine volume decreases.
4.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine osmolarity increases.
5.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), plasma osmolarity decreases.
6.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), the number of water channels in the tubule decreases.
7.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), water reabsorption from the tubule decreases.
8.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine volume increases.
9.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), urine osmolarity decreases.
10.
With an increase a decrease in the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH), plasma osmolarity increases.