「SHolroydAtWeilCornellMedQatar/Urology/Kidney/Tubules/WaterChannels/EffectOfDecrease」の版間の差分
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 27行目: | 27行目: | ||
[[メディア:WaterChannelsEffectOfDecreasing-3Eng.mp4|video showing the changes in plasma and urine after the decrease in vasopressin (ADH)]]<br> | [[メディア:WaterChannelsEffectOfDecreasing-3Eng.mp4|video showing the changes in plasma and urine after the decrease in vasopressin (ADH)]]<br> | ||
--> | --> | ||
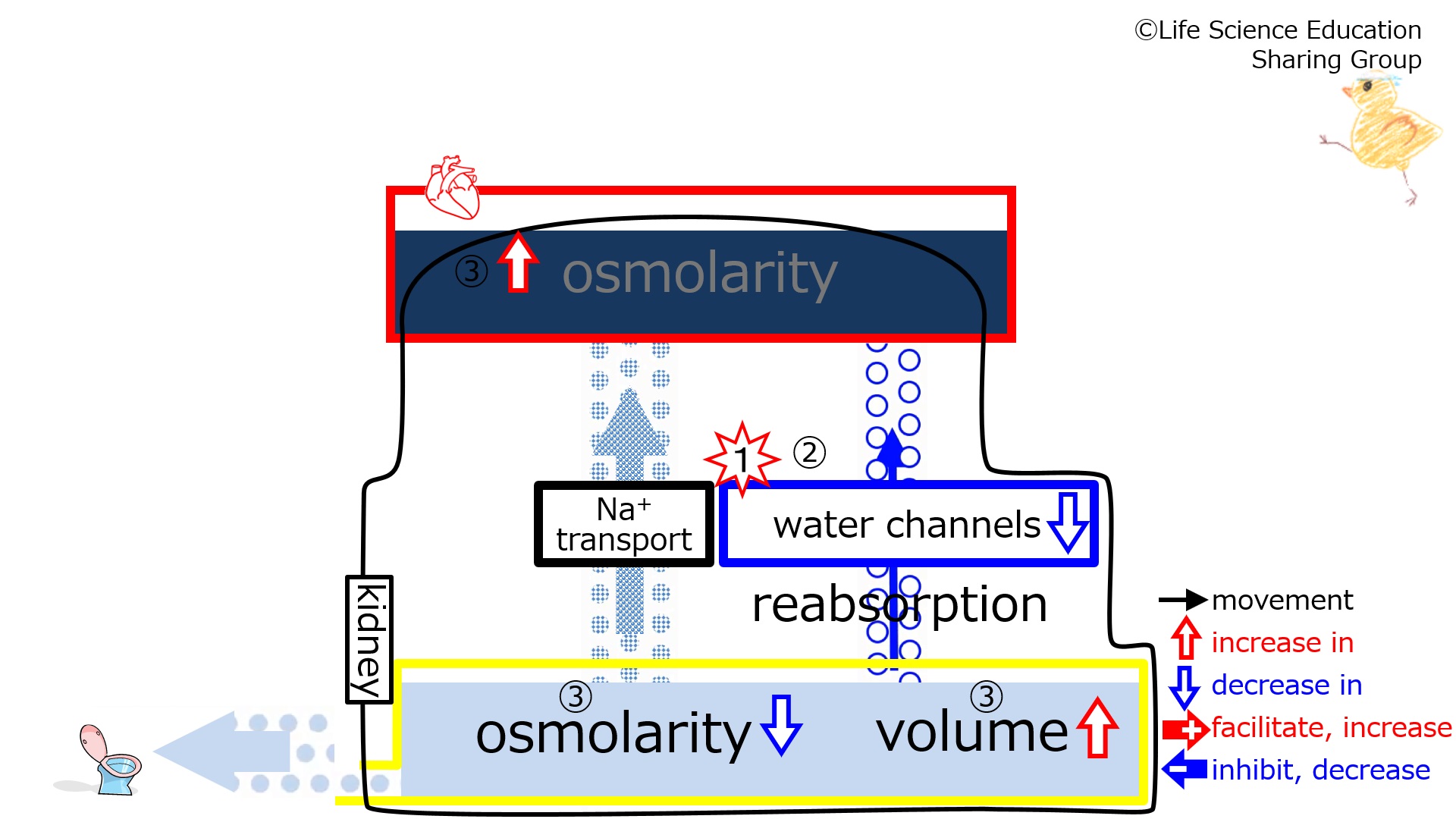
Step 3:With the decrease in water reabsorption, concentrated (hypertonic) solution enters the plasma. This increases plasma osmolarity (concentrated, hypertonic). Because concentrated (hypertonic) solution leaves the tubule due to reabsorption, the fluid remaining in the tubule has decreased osmolarity (diluted, hypotonic). Also, with the decrease in water reabsorption, there is more water remaining in the tubule. Overall, the urine becomes diluted and increases in volume.図の③:水分再吸収が減少し、濃い溶液(高張液)が血漿に入ります。これにより血漿浸透圧が上昇し(濃く、高張になり)ます。 | Step 3:With the decrease in water reabsorption, concentrated (hypertonic) solution enters the plasma. This increases plasma osmolarity (concentrated, hypertonic). Because concentrated (hypertonic) solution leaves the tubule due to water reabsorption, the fluid remaining in the tubule has decreased osmolarity (diluted, hypotonic). Also, with the decrease in water reabsorption, there is more water remaining in the tubule. Overall, the urine becomes diluted and increases in volume.図の③:水分再吸収が減少し、濃い溶液(高張液)が血漿に入ります。これにより血漿浸透圧が上昇し(濃く、高張になり)ます。 | ||
再吸収で濃い溶液(高張液)が尿細管から出るため、残る液の浸透圧が低下し(薄く、低張になり)ます。水分再吸収も減少するため、尿細管に残る水分は増加します。つまり尿は薄く、多量になります。 | 再吸収で濃い溶液(高張液)が尿細管から出るため、残る液の浸透圧が低下し(薄く、低張になり)ます。水分再吸収も減少するため、尿細管に残る水分は増加します。つまり尿は薄く、多量になります。 | ||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
2020年3月17日 (火) 14:50時点における版
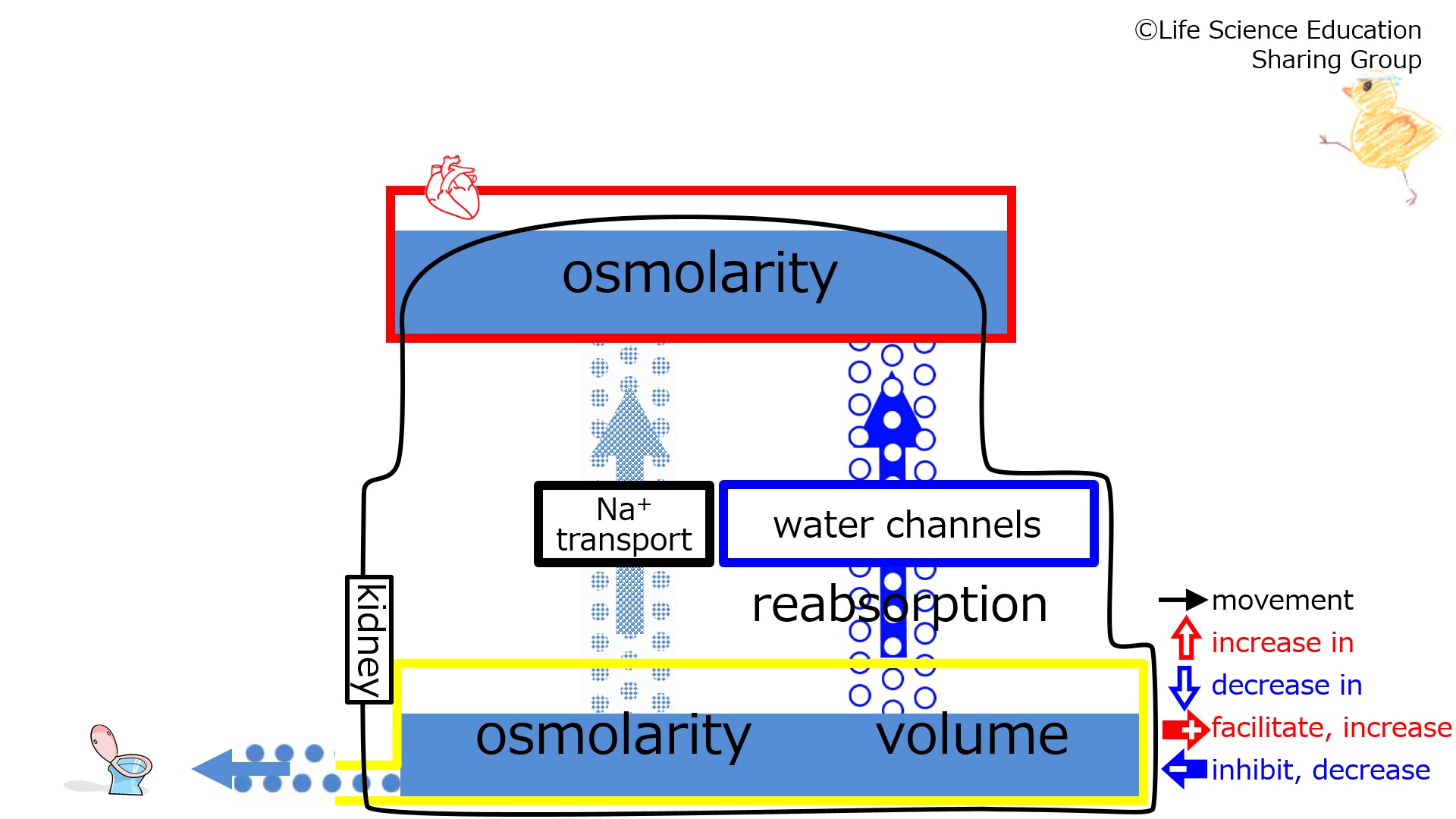
| With a decrease in the number of water channels, water reabsorption from the tubule decreases. 尿細管の水チャンネルが減少すると、尿細管からの水分再吸収は減少する。 |
Prior to the number of water channels decreasing (at baseline), we will make the assumption that the subject is in homeostasis with normal plasma and urine osmolarities (isotonic) and urine volume.水チャンネルの減少前(ベースライン)では恒常性が保たれていて、血漿浸透圧と尿浸透圧は正常(等張)、尿量も正常であるとしましょう。
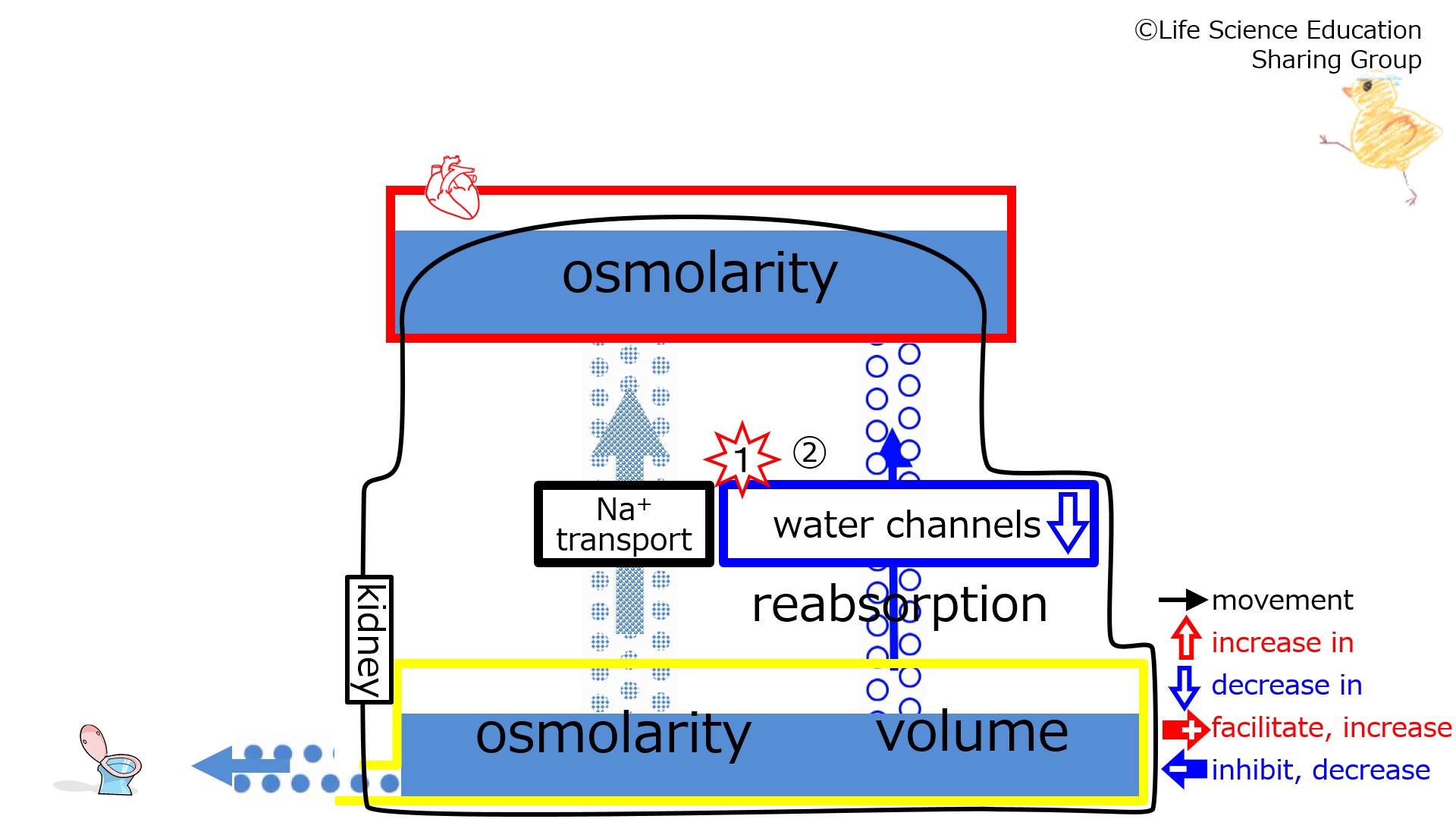
Step 1: Suppose that the number of water channels decreases. Step 2: With the decrease in the number of water channels, water reabsorption from the tubule decreases.図の①:最初に、水チャンネルが減少したとします。
図の②:水チャンネルの減少により尿細管からの水分再吸収は減少します。
Step 3:With the decrease in water reabsorption, concentrated (hypertonic) solution enters the plasma. This increases plasma osmolarity (concentrated, hypertonic). Because concentrated (hypertonic) solution leaves the tubule due to water reabsorption, the fluid remaining in the tubule has decreased osmolarity (diluted, hypotonic). Also, with the decrease in water reabsorption, there is more water remaining in the tubule. Overall, the urine becomes diluted and increases in volume.図の③:水分再吸収が減少し、濃い溶液(高張液)が血漿に入ります。これにより血漿浸透圧が上昇し(濃く、高張になり)ます。
再吸収で濃い溶液(高張液)が尿細管から出るため、残る液の浸透圧が低下し(薄く、低張になり)ます。水分再吸収も減少するため、尿細管に残る水分は増加します。つまり尿は薄く、多量になります。
Challenge Quiz
With a decrease in the number of water channels, water reabsorption from the tubule increases decreases .尿細管の水チャンネルが減少すると、尿細管からの水分再吸収は 増加 減少 する。
With a decrease in the number of water channels, urine volume increases decreases .尿細管の水チャンネルが減少すると、尿量は 増加 減少 する。
With a decrease in the number of water channels, urine osmolarity increases decreases .尿細管の水チャンネルが減少すると、尿の浸透圧は 上昇 低下 する。
With a decrease in the number of water channels, plasma osmolarity increases decreases .尿細管の水チャンネルが減少すると、血漿浸透圧は 上昇 低下 する。