「SHolroydAtWeilCornellMedQatar/Endocrinology/VasopressinADH/ControlToWaterIntake」の版間の差分
編集の要約なし |
編集の要約なし |
||
| 62行目: | 62行目: | ||
//LEVEL:3 | //LEVEL:3 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
After intake of water, the plasma osmolarity {~=decreases~increases}. The effect would be the {=same as~opposite to} that of ADH, water channels and reabsorption of water by the kidney, which {=decreases~increases} plasma osmolarity | After intake of water, the plasma osmolarity {~=decreases~increases}. The effect would be the {=same as~opposite to} that of ADH, water channels and reabsorption of water by the kidney, which {=decreases~increases} plasma osmolarity. The effect of (the synthesis, secretion and blood concentration of) ADH would be {too little~=too much}. Negative feedback {~increases~=decreases} (synthesis, secretion, blood concentration of) ADH. This in turn {increases~=decreases} the production of water channels in the kidney causing {increased~=decreased} water reabsorption. Urine osmolarity will {increase~=decrease} while volume will {~=increase~decrease}. This will {decrease~=increase} plasma osmolarity, {~=returning to normal~separating from normal}. | ||
</GIFT> | </GIFT> | ||
2019年6月5日 (水) 13:39時点における版
| When plasma osmolarity is decreased by intake of water, the negative feedback decreases (synthesis, secretion, blood concentration of) ADH. |
video prior to intake of water
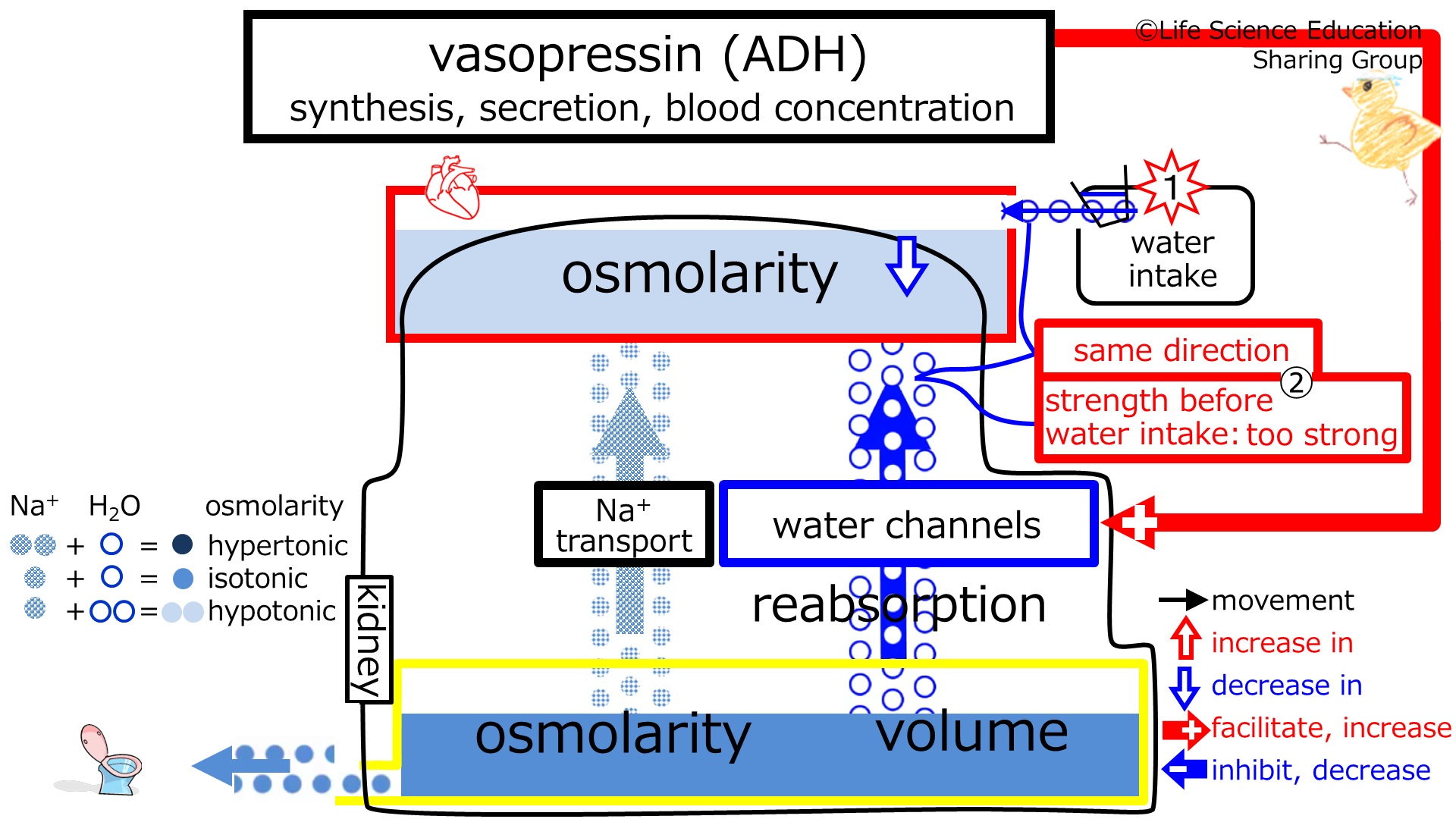
Prior to intake of water, we assume our subject is in homeostasis with normal plasma and urine osmolarities and volumes.
video just after intake of water
Steps 1 and 2: Water was taken. Water will enter the plasma and its osmolarity will decrease.
Both intake of water and the ADH, water channels, and reabsorption of water by the kidney will decrease plasma osmolarity, having the same effect. Thus, in this case with low plasma osmolarity, the plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect of ADH, water channels, and reabsorption would be too much.
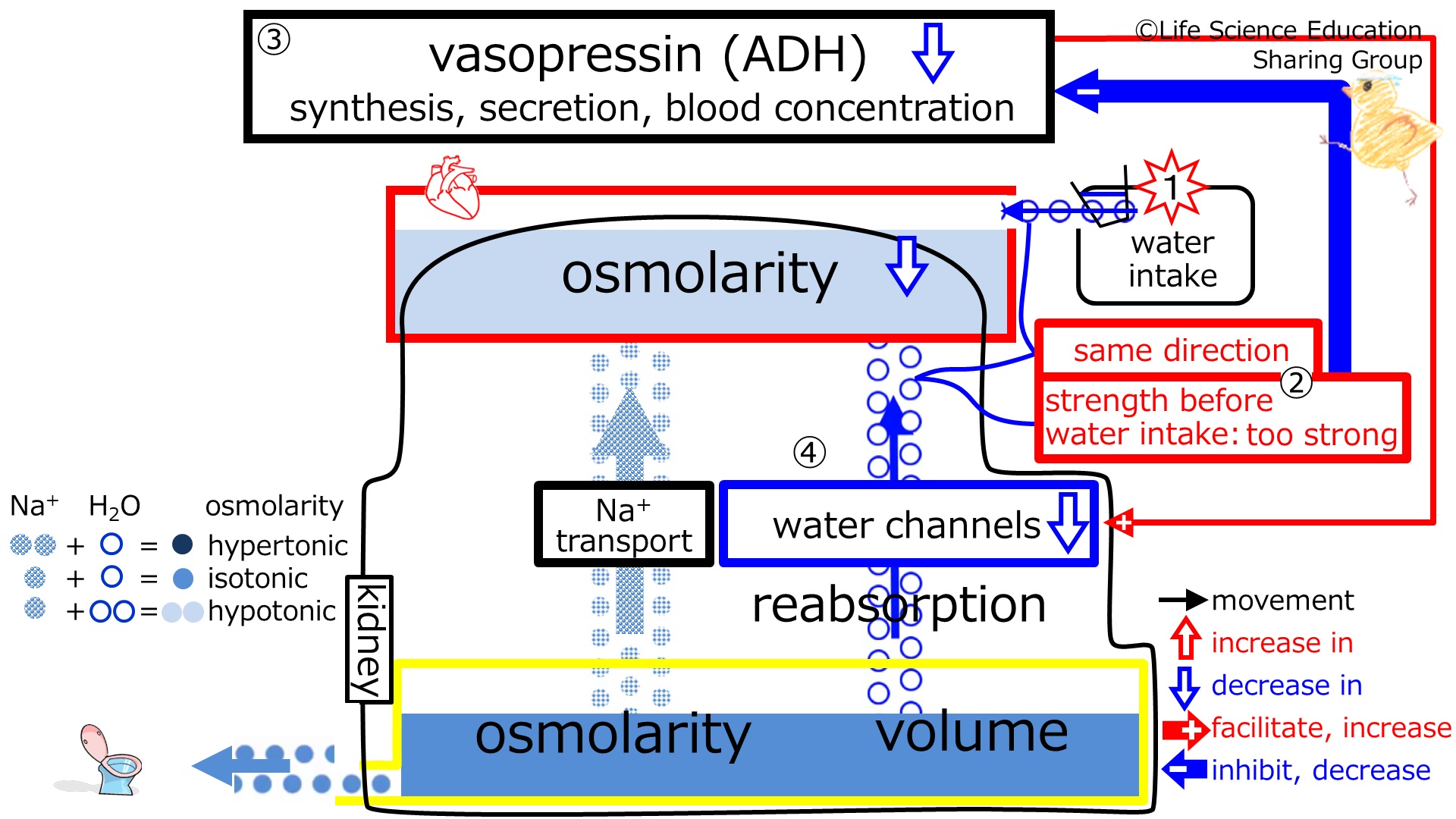
video just after ADH decreased responding to intake of water
Steps 3 and 4: With too much effect of ADH, water channels, and reabsorption, the negative feedback decreases (synthesis, secretion, blood concentration of) ADH. The water channels-increasing effect of ADH will decrease, decreasing the number of water channels. This decreases the reabsorption of water by the kidney.
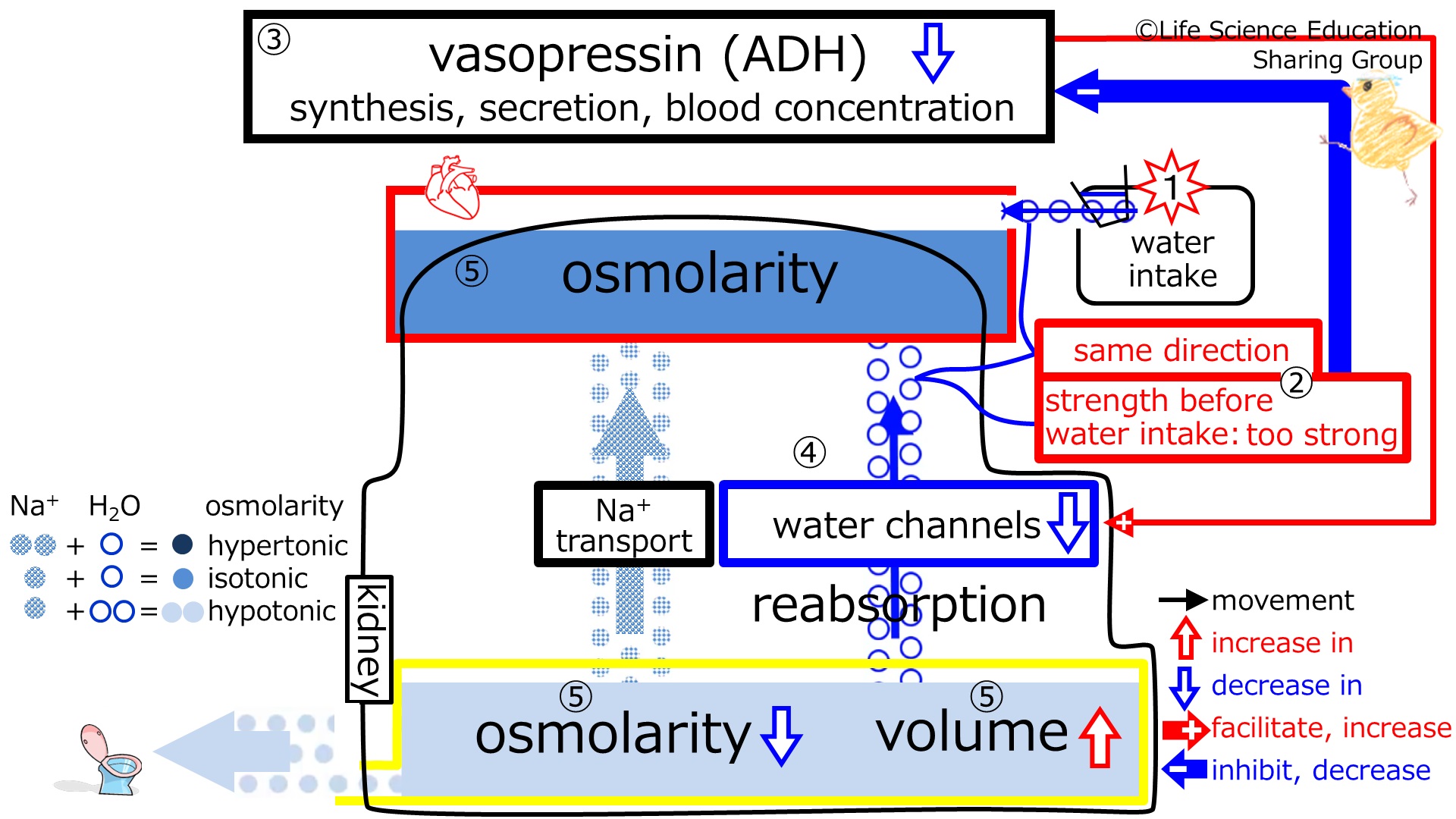
video showing the changes in plasma and urine after ADH decreased responding to intake of water
Step 5: The ratio of Na+ to water reabsorption by the kidney increases. This means plasma osmolarity increases. The decreased plasma osmolarity from intake of water will increase returning to normal.
Because a higher ratio of Na+ is reabsorbed the fluid left in the tubule now has a lower osmolarity. The decrease in the number of water channels decreases water reabsorption so there is more water. Overall, the urine becomes less concentrated and high volume.
Challenge Quiz
After intake of water, negative feedback increases decreases (synthesis, secretion, blood concentration of) ADH.
After intake of water, negative feedback increases decreases water channels channels in the kidney.
After intake of water, negative feedback increases decreases water reabsorption by the kidney.
After intake of water, negative feedback increases decreases urine volume.
After intake of water, negative feedback increases decreases urine osmolarity.
After intake of water, negative feedback increases decreases plasma osmolarity.
After intake of water, the plasma osmolarity decreases increases . The effect would be the same as opposite to that of ADH, water channels and reabsorption of water by the kidney, which decreases increases plasma osmolarity. The effect of (the synthesis, secretion and blood concentration of) ADH would be too little too much . Negative feedback increases decreases (synthesis, secretion, blood concentration of) ADH. This in turn increases decreases the production of water channels in the kidney causing increased decreased water reabsorption. Urine osmolarity will increase decrease while volume will increase decrease . This will decrease increase plasma osmolarity, returning to normal separating from normal .