「Nerv06/introduction/terms regarding membrane potential」の版間の差分
Soichi.Nakatake (トーク | 投稿記録) 編集の要約なし |
Soichi.Nakatake (トーク | 投稿記録) 編集の要約なし |
||
| 23行目: | 23行目: | ||
//LEVEL: | //LEVEL:4 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
When the membrane potential depolarizes even a small amount from the resting membrane potential, the action potential is always generated. {~true.=false} | When the membrane potential depolarizes even a small amount from the resting membrane potential, the action potential is always generated. {~true.=false} | ||
2014年3月7日 (金) 12:32時点における版
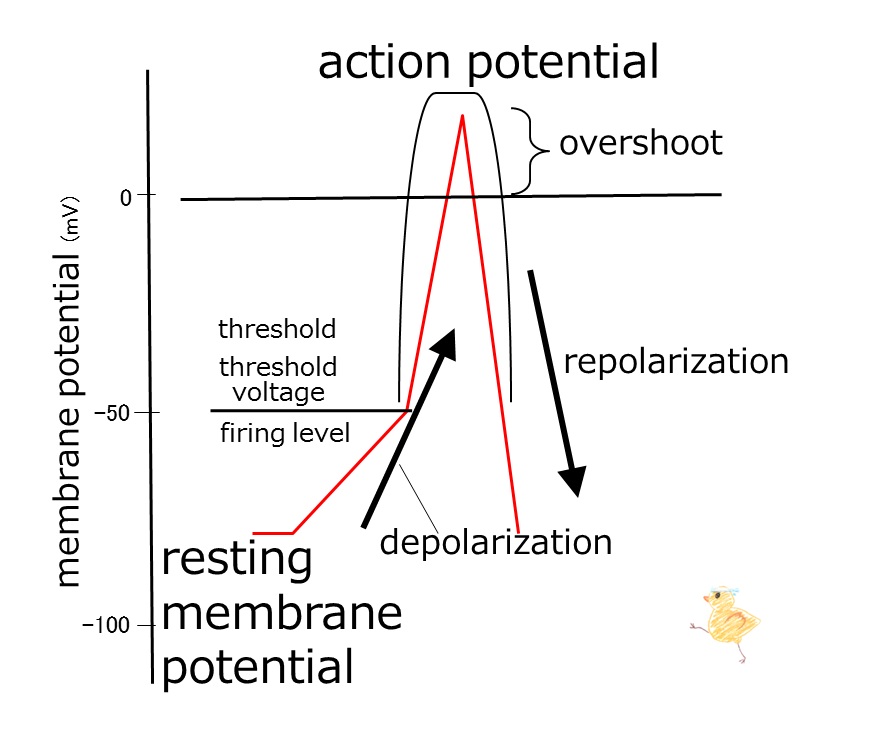
Inside the cell membrane at rest, a negative potential is being generated. With stimulation, this negative potential decreases. This is called depolarization. When the membrane potential decreases to a certain level, an active potential, called the action potential is generated. The voltage at which this transaction occurs, is called the threshold, threshold voltage, or firing level.
The characteristics of the action potential are rapid depolarization and overshoot. Overshoot means switching of the electric polarity inside and outside the cell membrane, making it positive inside.
After overshoot, the negative polarity increases rapidly, and the action potential ends, returning to the resting membrane potential. This process is called the re-polarization.
Challenge Quiz
The process of the (absolute voltage of the) resting membrane potential decreasing and the neuron being activated is called hyperpolarization.depolarization .
The neuron cell membrane repolarizes.depolarizes when stimulated.
When the membrane potential depolarizes to the firing level (threshold, threshold voltage), the action potential is. is not generated.
When the membrane potential depolarizes even a small amount from the resting membrane potential, the action potential is always generated. true.false
When a neuron is stimulated and an overshoot is generated, the electrical potential is switched and inside the membrane becomes positive. negative .
After overshoot, the membrane depolarizes.repolarizes to the resting membrane potential.