「Endocrinology/VasopressinADH/ControlToSweating/basic」の版間の差分
細 (Admin がページ「SHolroydAtWeilCornellMedQatar/Endocrinology/VasopressinADH/ControlToSweating/basic」を「Endocrinology/VasopressinADH/ControlToSweating/basic」に、リダイレクトを残さずに移動しました) |
編集の要約なし |
||
| (同じ利用者による、間の2版が非表示) | |||
| 6行目: | 6行目: | ||
[[ファイル:SweatingBeforeBasicFeedbackToADH-Eng.jpg|left|500px]] | [[ファイル:SweatingBeforeBasicFeedbackToADH-Eng.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
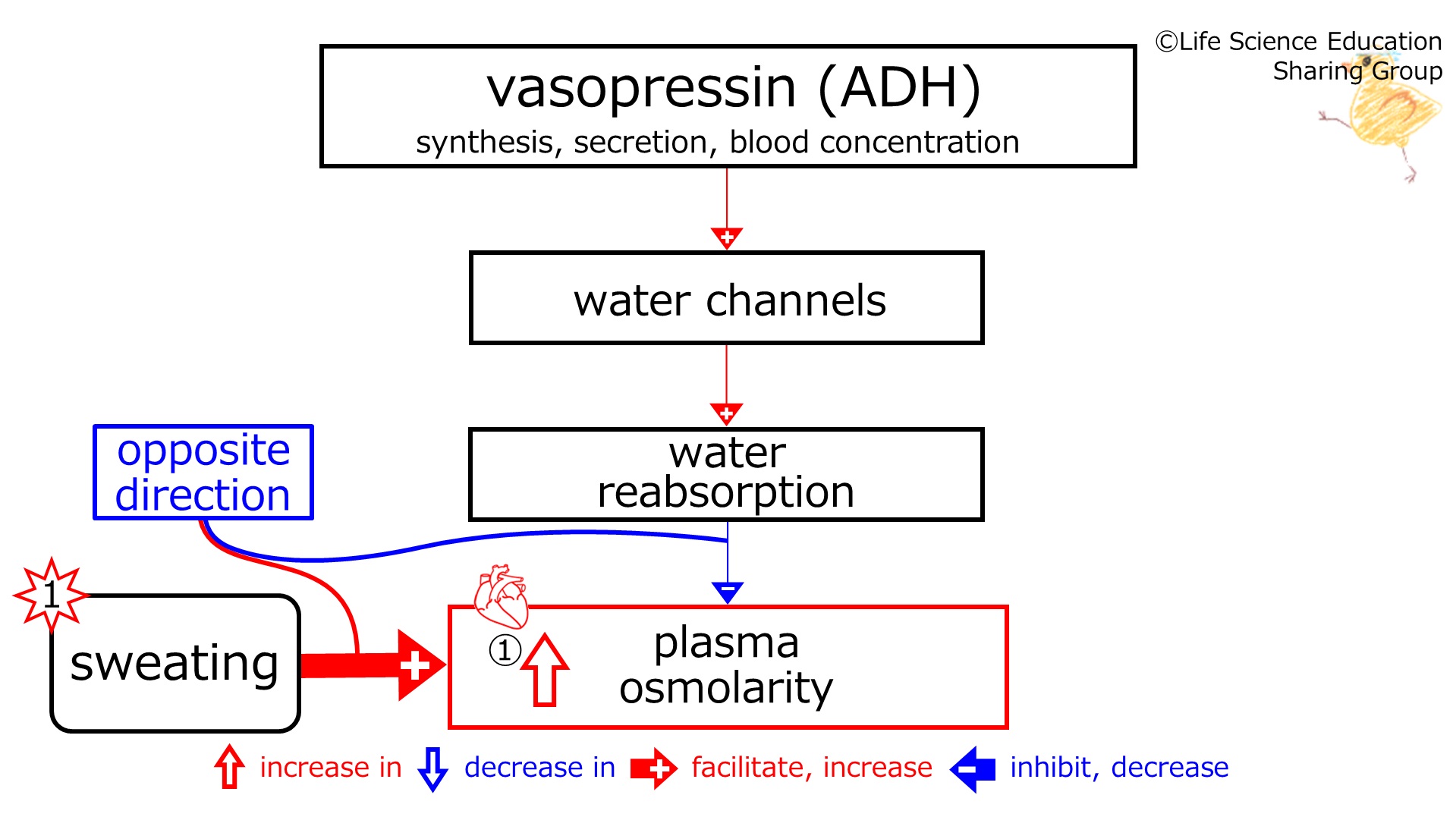
1st star (illustration): Subject sweated. With sweating, plasma osmolarity increases. (Synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of )vasopressin (ADH) (increases water channels. Water channels increase water reabsorption. Water reabsorption) decreases plasma osmolarity.<br> | |||
①(illustration): These are in the <font color="#00f">opposite direction (blue)</font>. | |||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
[[ファイル:SweatingDuringBasicFeedbackToADH-Eng.jpg|left|500px]] | [[ファイル:SweatingDuringBasicFeedbackToADH-Eng.jpg|left|500px]] | ||
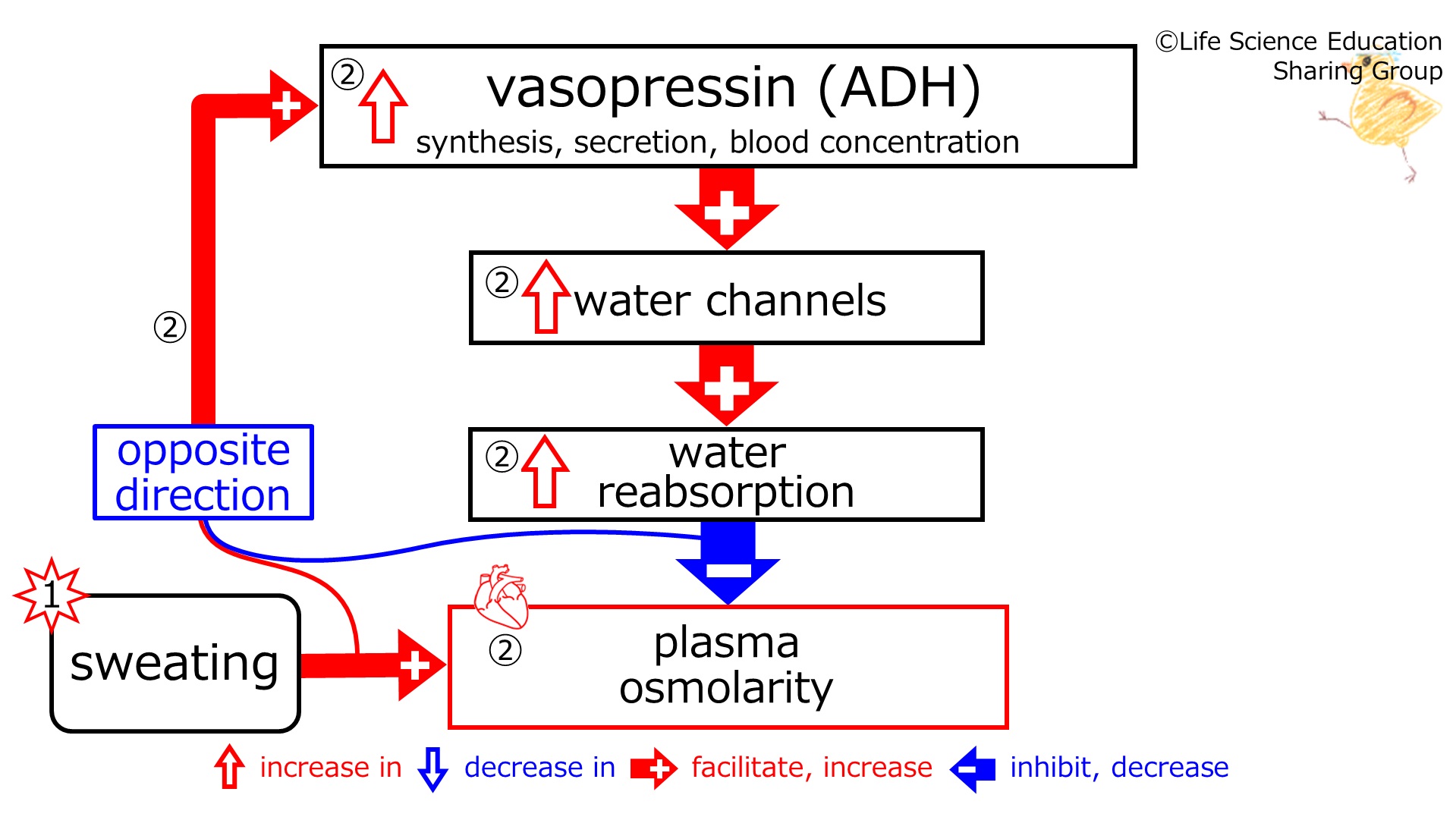
② Since these | ②(illustration): Since these are in the <font color="#00f">opposite direction (blue)</font>, negative feedback <font color="#ff0000">increases (red)</font> (synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of vasopressin (ADH).<br> | ||
<br> | |||
With the increase in (the synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of)vasopressin (ADH), (water channel-increasing effect is strengthened, and water channels are increased. With the increase in water channels, water reabsorption-increasing effect is strengthened, and water absorption is increased. With the increase in water reaborption), plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect is strengthened.<br> | |||
<br> | |||
Because of this control, the increased plasma osmolarity decreases (towards that before sweating). | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
Namely, the initial change (the increase in plasma osmolarity) decreases (red upward unfilled arrow disappears).<br> | |||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
Similar to cooler (function) being increased when room temperature is increased (summer), this also is <font color="#00f">blue</font>→<font color="#ff0000">red</font> negative feedback. | |||
{{QuizTitle}} | {{QuizTitle}} | ||
<GIFT> | <GIFT> | ||
//LEVEL: | //LEVEL:3 | ||
//RAND | //RAND | ||
発汗により血漿浸透圧は{~=上昇~低下}し、バソプレッシン、抗利尿ホルモン ADH(は水チャンネルを{~=増加~減少}させ、水チャンネルは水分再吸収を{~=増加~減少}させます。水分再吸収)は血漿浸透圧を{~上昇~=低下}させる。これらは{~同じ~=逆の}方向なので、負のフィードバックはバソプレッシン(抗利尿ホルモン anti-diuretic hormone, ADH)の生成、内分泌、血中濃度を{~=亢進~低下}させる。水チャンネルが{~=増加~減少}、水分再吸収が{~=増加~減少}し、水分再吸収の血漿浸透圧{~上昇~=低下}作用が{~=増強~減弱}し、この調節により、{~=上昇~低下}していた血漿浸透圧は、(発汗前の浸透圧へ向けて){~上昇~=低下}する。要するに、最初の変化(血漿浸透圧の{~=上昇~低下})は{~大きくなる~=小さくなる(消える)}。 | |||
</GIFT> | </GIFT> | ||
2024年4月1日 (月) 10:10時点における最新版
| With sweating, the (blue→red) negative feedback increases (the synthesis, secretion, and blood concentration of) vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone, ADH). |
1st star (illustration): Subject sweated. With sweating, plasma osmolarity increases. (Synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of )vasopressin (ADH) (increases water channels. Water channels increase water reabsorption. Water reabsorption) decreases plasma osmolarity.
①(illustration): These are in the opposite direction (blue).
②(illustration): Since these are in the opposite direction (blue), negative feedback increases (red) (synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of vasopressin (ADH).
With the increase in (the synthesis, secretion, and concentration in blood of)vasopressin (ADH), (water channel-increasing effect is strengthened, and water channels are increased. With the increase in water channels, water reabsorption-increasing effect is strengthened, and water absorption is increased. With the increase in water reaborption), plasma osmolarity-decreasing effect is strengthened.
Because of this control, the increased plasma osmolarity decreases (towards that before sweating).
Namely, the initial change (the increase in plasma osmolarity) decreases (red upward unfilled arrow disappears).
Similar to cooler (function) being increased when room temperature is increased (summer), this also is blue→red negative feedback.
Challenge Quiz
発汗により血漿浸透圧は 上昇 低下 し、バソプレッシン、抗利尿ホルモン ADH(は水チャンネルを 増加 減少 させ、水チャンネルは水分再吸収を 増加 減少 させます。水分再吸収)は血漿浸透圧を 上昇 低下 させる。これらは 同じ 逆の 方向なので、負のフィードバックはバソプレッシン(抗利尿ホルモン anti-diuretic hormone, ADH)の生成、内分泌、血中濃度を 亢進 低下 させる。水チャンネルが 増加 減少 、水分再吸収が 増加 減少 し、水分再吸収の血漿浸透圧 上昇 低下 作用が 増強 減弱 し、この調節により、 上昇 低下 していた血漿浸透圧は、(発汗前の浸透圧へ向けて) 上昇 低下 する。要するに、最初の変化(血漿浸透圧の 上昇 低下 )は 大きくなる 小さくなる(消える) 。